Fig. 5. Effects of chronic excessive alcohol drinking on fecal metabolome.
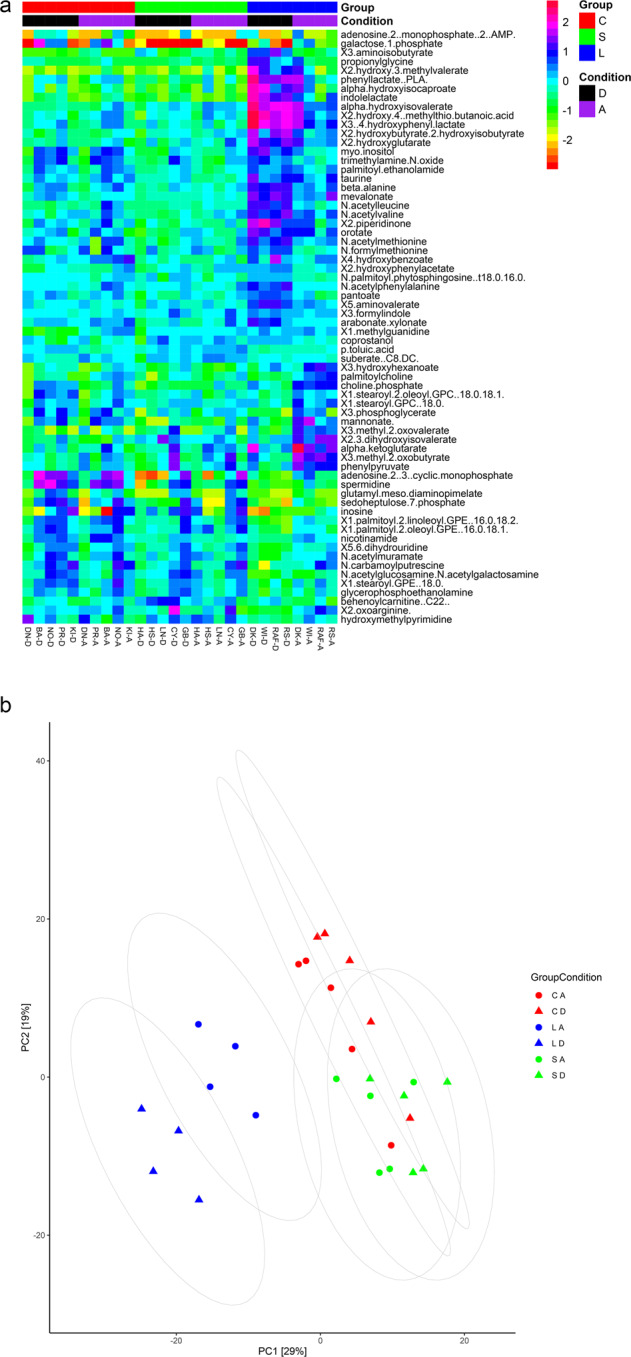
a Heatmap showing those metabolites (N = 63), out of the 534 identified, which achieved statistical significance (FDR-adjusted p < 0.01) in the group x condition interaction in the linear mixed models (LMMs). The long-term alcohol drinking group (L) is depicted in blue, the short-term alcohol drinking group (S) in green, and the control group (C) in red. The drinking condition (D) is depicted in black and the abstinence condition (A) in purple. b Score plot between the selected first two principal components (PCs) based on the output from the linear mixed models (LMMs). Group L is depicted in blue, group S in green, and group C in red. Triangles represent the drinking condition for each group (LD, SD, CD), circles represent the abstinence condition for each group (LA, SA, CA). Percent explained variance is reported in brackets on first (x axis) and second (y axis) principal component axis.
