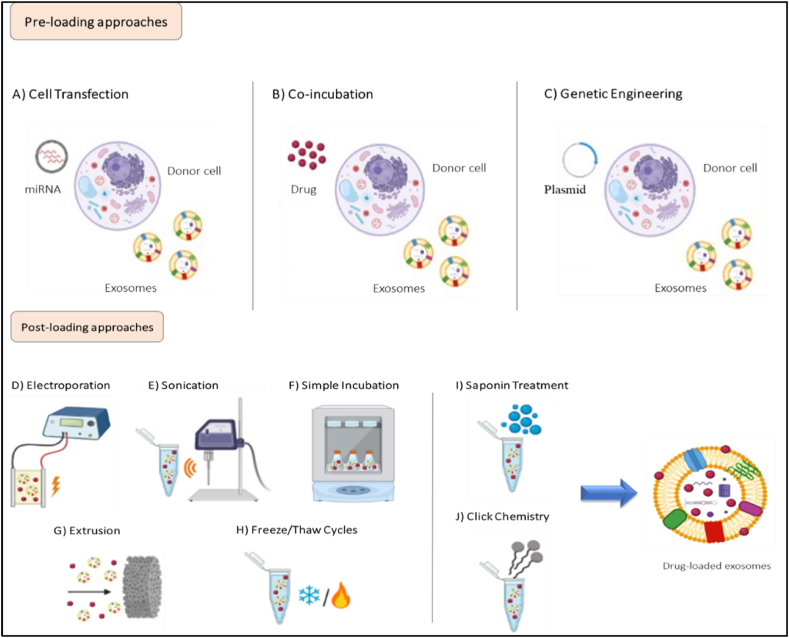
Fig. 4.
Various methods of loading cargoes in exosomes for therapeutic delivery. In pre-loading methods, therapeutic molecules are incorporated into donor cells before the production of exosomes. During exosome biogenesis, incorporated molecules are packaged within exosomes to be used for therapeutic purposes. miRNA, siRNA, and mRNA can be loaded into parent cells through transfection (A). Moreover, some parent cells can uptake drug molecules by passive diffusion when they are co-incubated (B). Engineered exosomes can be produced through introduction of plasmids into parent cells to induce the expression of therapeutic molecules in exosomes (C). In post-loading methods, drug molecules are loaded directly into exosomes after isolation through physical and chemical methods. Physical methods such as electroporation (D), sonication (E), simple incubation (F), extrusion (G), and freeze/thaw cycles (H) increase exosome membrane permeability to uptake drug molecules. Chemical methods such as saponin treatment (I) and click chemistry (J) can also be used. Saponin treatment promotes the formation of pores due to its interaction with membrane cholesterol, while click chemistry enables the binding of drug molecules to the external surface of the exosome membrane. Created withBioRender.com.