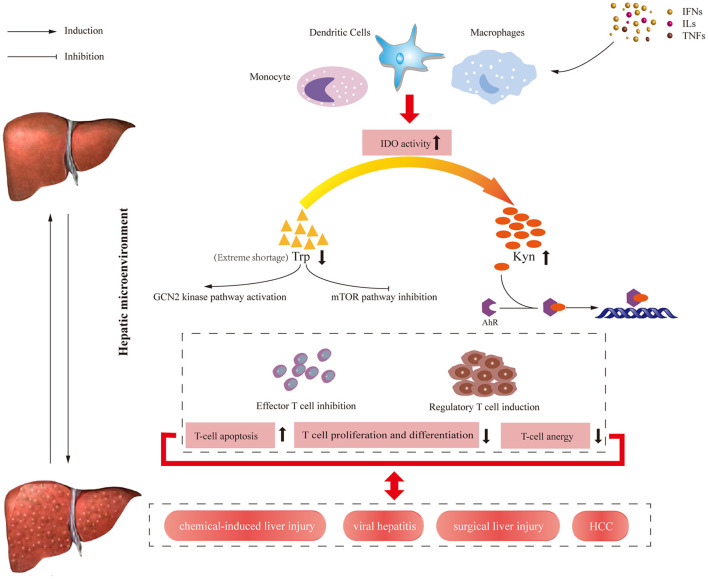
Figure 2.
Overview of immune regulation pathways induced by IDO enzyme in humans. At the transcriptional level, IDO enzyme is expressed by various cells of the immune system and activated by cytokines and other immunomodulatory molecules such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IFN-γ. On the one hand, IDO activity results in decreasing available Trp level, which activates the GCN2 kinase pathway and inhibits the mTOR pathway, leading to the reduced number of antigen-specific T cells. On the other hand, increasing Kyn level and KP metabolite concentrations induced by IDO activate AHR pathway, leading to the increased number of regulatory T cell. The results of these signal pathways contribute to the apoptosis of effector T cells and proliferation regulatory T cells. IFNs, interferons; ILs, interleukins; TNFs, tumor necrosis factors; IDO, Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; Trp, tryptophan; Kyn, kynurenine; GCN2, general control non-depressible; AHR, aryl hydrocarbon receptor; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin.