FIGURE 1.
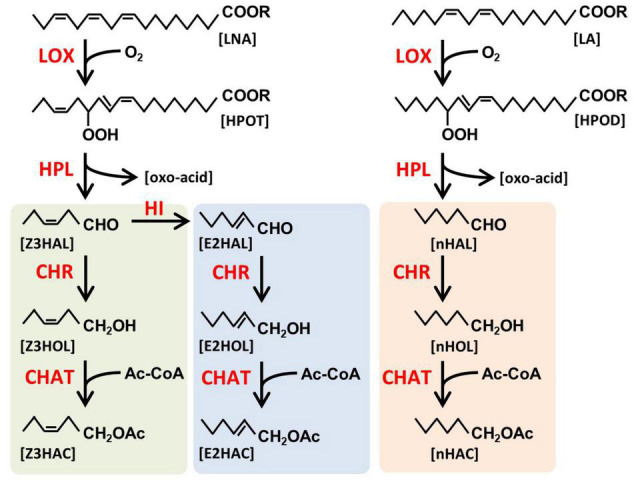
Biosynthetic pathway of green leaf volatiles (GLVs). GLVs are fatty acid-derived volatiles. Linolenic acid (LNA) and linoleic acid (LA) are oxidized by lipoxygenases (LOX) to form 13-hydroperoxy octadecatrienoic acid (HPOT) and 13-hydroperoxy octadecadienoic acid (HPOD), respectively, and subsequently cleaved by hydroperoxide lyase (HPL) to form green leaf aldehydes, (Z)-3-hexenal (Z3HAL), and n-hexanal (nHAL), respectively. Z3HAL could be converted into (E)-2-hexenal (E2HAL) by Z3:E2-hexenal isomerase (HI). Three forms of green leaf aldehydes [Z3HAL (green), E2HAL (blue), and nHAL (orange)] are reduced by cinnamaldehyde and hexenal reductase (CHR) to form green leaf alcohols [(Z)-3-hexenol (Z3HOL), (E)-2-hexenol (E2HOL), and n-hexanol (nHOL), respectively]. The green leaf alcohols are subsequently acylated by acetyl CoA:(Z)-3-hexen-1-ol acetyltransferase (CHAT) to form (Z)-3-hexenyl acetate (Z3HAC), (E)-2-hexenyl acetate (E2HAC), and n-hexyl acetate (nHAC) with acetyl CoA as an acyl donor.
