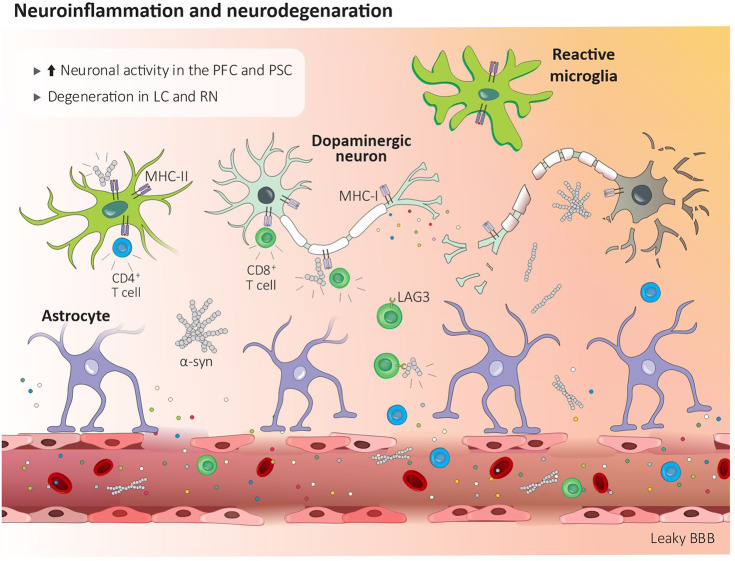
Figure 2.
Central inflammation in Parkinson’s disease. Peripheral inflammation increases the blood brain barrier permeability which facilitates the infiltration of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. Lag3+ CD8 T cells help disseminate α-syn centrally, while brain circulating α-syn-reactive CD4+ and CD8+ T cells recognize MHC-II bound peptides on microglia and MHC-I on dopaminergic neurons. Modified α-synuclein acts as a damage-associated molecular pattern, and via its action on receptors found on microglia and macrophages, induces cytokines release and neurodegeneration. BBB, blood brain barrier; LAG3, lymphocyte activation gene-3; LC, locus coeruleus; MHC-I, major histocompatibility complex I; MHC-II, major histocompatibility complex II; PFC, prefrontal cortex; PSC, primary somatosensory cortex; RN, raphe nuclei; α-syn, α-synuclein .