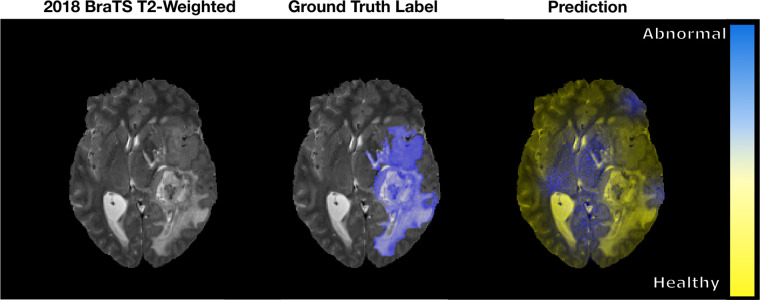
Figure 1:
An example of a pixel-wise classification output fused to a sample axial T2-weighted MRI section from the 2018 Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention Society Multimodal Brain Tumor Image Segmentation (BraTS) dataset (16,17). The ground truth abnormality is shown in blue. The prediction from the untrained network classifies the abnormal and healthy brain tissues as blue and yellow, respectively. As seen, the network classifies healthy brain tissue as abnormal when there is no basis to do so.