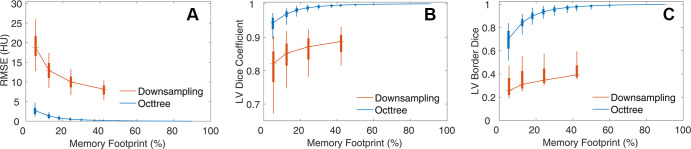
Figure 5:
Comparison of image and segmentation representation between spatial downsampling-upsampling and octree compression. (A) Use of OctNet leads to lower (P < .001) image distortion as measured by root mean square error (RMSE) than spatial downsampling-upsampling across all levels of compression. (B) Segmentation accuracy of the left ventricular (LV) label is higher (P < .001) with octree compression than with spatial downsampling. (C) Octrees preserve boundary segmentation Dice coefficients better (P < .001) than spatial downsampling. Boxes represent the interquartile range (25th to 75th percentile), and whiskers depict the 5th- and 95th-percentile range.