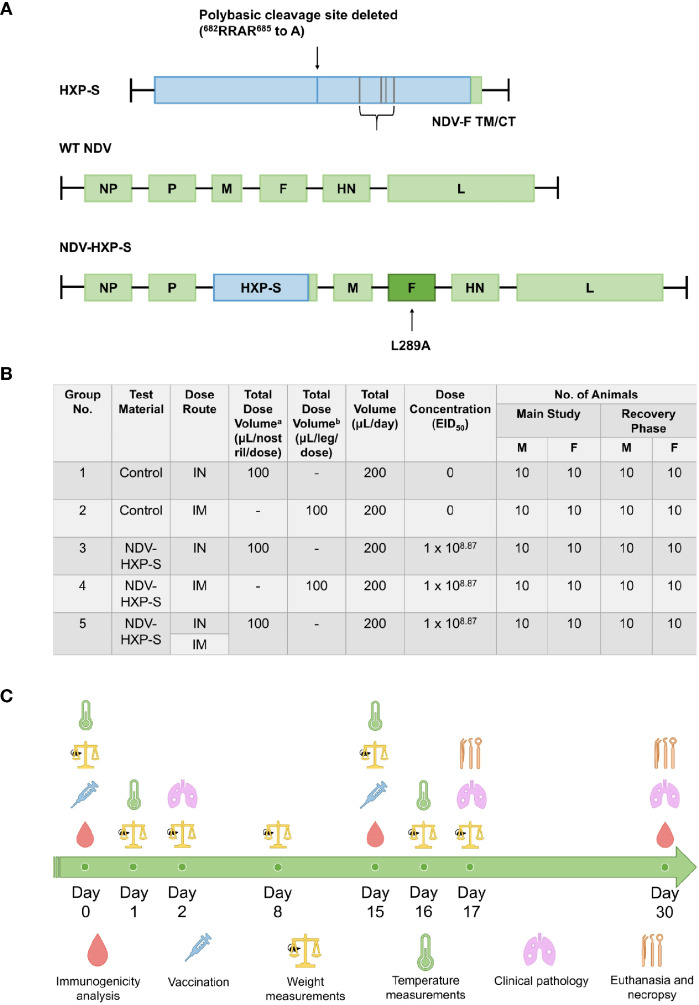
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of NDV-HXP-S production and testing in rats. (A) Vector design. The S/F chimera was created by fusing the spike protein ectodomain (S), containing HexaPro stabilizing mutations, to the transmembrane domain and cytoplasmic tail (TM/CT) of the Newcastle Disease Virus (NDV) fusion (F) protein via a short GGGGS linker. The three arginines (R) in the polybasic cleavage site (RRAR) were removed to eliminate the cleavage site. The construct was termed HXP-S, which is codon optimized for mammalian expression. The HXP-S nucleotide sequence was incorporated between the P and M genes of the La Sota NDV genome carrying the L289A mutation in the F protein. (B) Groups distribution. Rats were separated into five groups: intranasal (IN) control (group 1), intramuscular (IM) control (group 2), IN vaccinated (group 3), IM vaccinated (group 4), and IN-IM vaccinated (group 5). Rats receiving the vaccine by uneven administration routes first received the intranasal dose at day 0, followed by the intramuscular dose at day 15. Intranasal dose volume was administered to each nostril twice at 50 µL/occasion, 30 ± 5 minutes apart, for the total dose volume of 100 µL/naris, or 200 µL total. Intramuscular dose volume was administered to the thigh muscles of both hind legs, for the total dose volume of 100 µL/leg, or 200 µL total. (C) Experimental design. All the groups received a vaccine prime at day 0 followed by a boost at day 15. Serum samples were collected for immunogenicity analyses at days 0, 15, and 30 after the first vaccine dose administration. Weight measurements were performed on days 0, 1, 2, 8, 15, 16, and 17 post-vaccination. Body temperatures (°C) were measured at 0-, 6- and 24-hours post-dosage, after both the prime and boost vaccine administrations. Clinical pathology assessments were performed on days 2, 17, and 30 following the first vaccination. Rats were euthanized on day 17 and day 30 for the main and recovery groups, respectively.