Fig. 6.
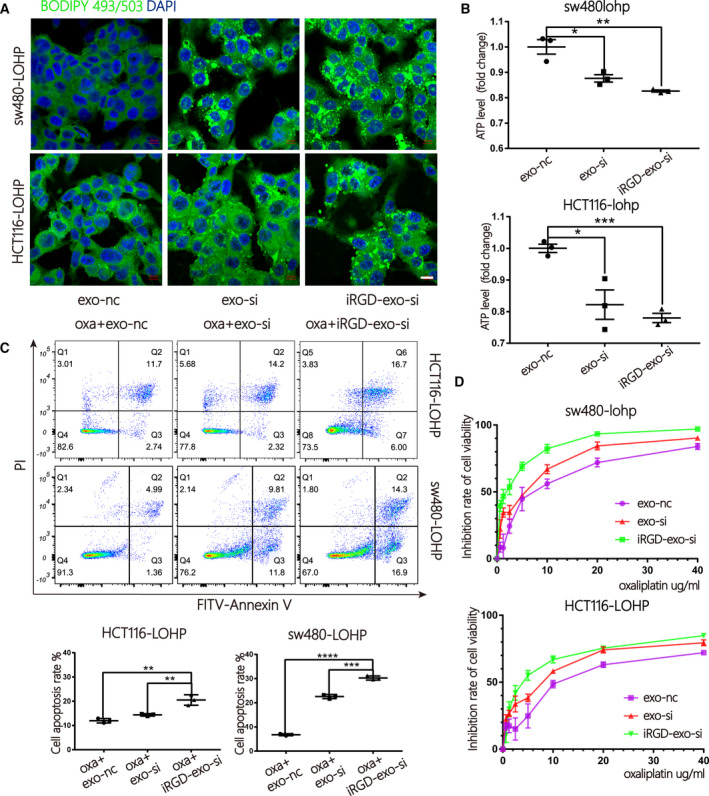
Improved inhibition of FAO by iRGD‐exo‐si in colon cancer. (A) Cells treated with iRGD/control‐exo‐si were stained with BODIPY‐493/503 (dyes of fatty acids, 1 µg·mL−1, green) and DAPI (blue) and imaged by confocal microscopy (scale bar = 10 μm). (B) A CellTiter‐Glo Luminescent Cell Viability Assay was used to test the total ATP production of cells treated with iRGD/control‐exo‐si (n = 3, mean ± SEM, t‐test). (C) Apoptosis ratio by flow cytometry in sw480‐lohp/HCT116‐lohp cells treated with iRGD/control‐exo‐si and oxaliplatin (n = 3, mean ± SEM, t‐test). (D) CCK‐8 assay of the inhibition ratio by oxaliplatin in sw480‐lohp/HCT116‐lohp cells treated with iRGD/control‐exo‐si (n = 3, mean ± SEM, t‐test). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001.
