FIGURE 1.
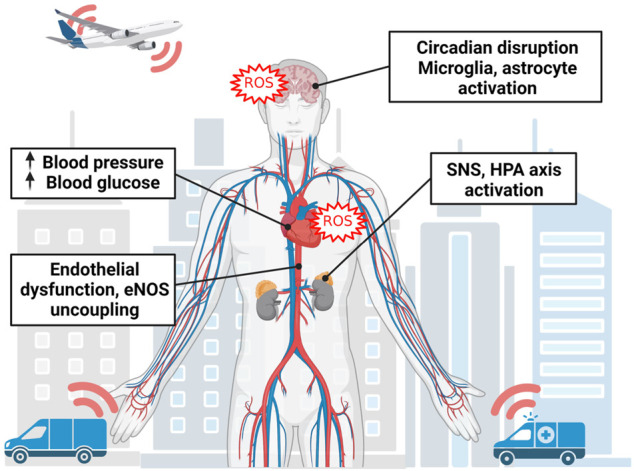
Overall mechanism of noise-triggered adverse health effects. Noise perception starts in the brain leading to neuronal activation in association with disruption of circadian rhythms (especially by nighttime noise causing sleep deprivation and fragmentation), neuroinflammation and cerebral oxidative stress. Noise activates down-stream stress responses such as activation of the sympathetic nervous system (SNS) and the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis leading to stress hormone release such as catecholamines and cortisol with secondary activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. This cascade will converge in oxidative stress and inflammation in association with eNOS uncoupling, endothelial dysfunction and high blood pressure as well as hyperglycemia, well-known triggers of cardiovascular sequela. Image was created using Biorender.com.
