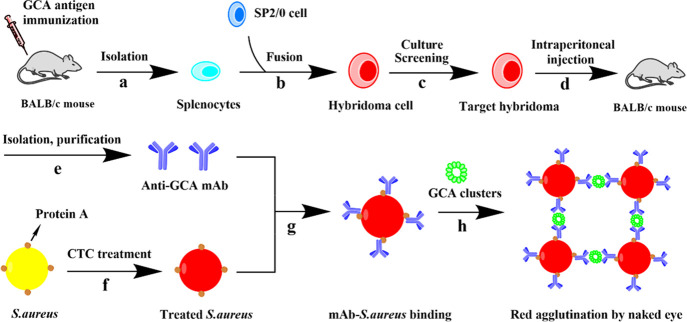
Scheme 1. Schematic Illustration of GCA Bioprobe Preparation and Visually Enhanced Coagglutination Test of GCA,,,,,,,
Splenocytes were isolated from the spleen of BALB/c mice immunized with a GCA antigen.
Hybridoma cells were obtained through the fusion of splenocytes and SP2/0 cells.
The target hybridoma cloned was acquired by further culturing and screening.
The target hybridoma cloned was injected into mice to collect ascites containing antibodies by intraperitoneal injection.
The anti-GCA monoclonal antibody was isolated and purified from ascites.
Staphylococcus aureus (S.aureus) turns red after CTC treatment.
A probe (mAb-S.aureus conjugate) is formed due to the combination of protein A on S.aureus and the Fc segment of the mAb.
When the probe and a sample containing GCA (probably forming a smaller cluster due to non-covalent interactions between GCA) is mixed on a glass slide, a larger red cluster is formed on the slide due to the recognition between the GCA cluster and anti-GCA, allowing us to detect the GCA by naked-eye visualization of the red spots.