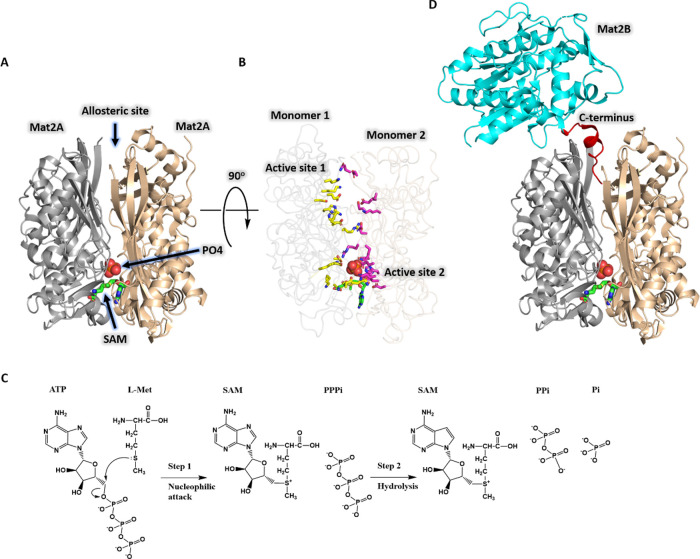
Figure 1.
The structure and overall reaction catalyzed by human Mat2A. (A) The dimeric structure of Mat2A (cartoon representation) with the products SAM (stick representation, with green carbon atoms) and Pi (sphere representation, with orange phosphorus and red oxygen atoms) occupying one active site. Mat2A monomers are colored in gray and wheat. (B) As in panel A, viewed from the allosteric site (90° rotation) to show the two active sites of the Mat2A homodimer with one site empty and one site occupied by SAM and Pi. Mat2A main chains are transparent to clearly show the active sites. Active site residues are shown with side chains in stick representation with yellow or pink carbon atoms. (C) As in panel A with Mat2B bound via its C-terminus to an allosteric site in the Mat2A dimer. Mat2B is colored in cyan and its C-terminus is red (PDB ID 4KTT).13 (D) The overall reaction catalyzed by Mat2A occurs via two distinct steps. The first step involves the sulfur atom of l-Met performing a nucleophilic attack on ATP, forming the product SAM and the intermediate tripolyphosphate (PPPi). The second step involves the hydrolysis of PPPi that precedes the release of products SAM, PPi, and Pi.