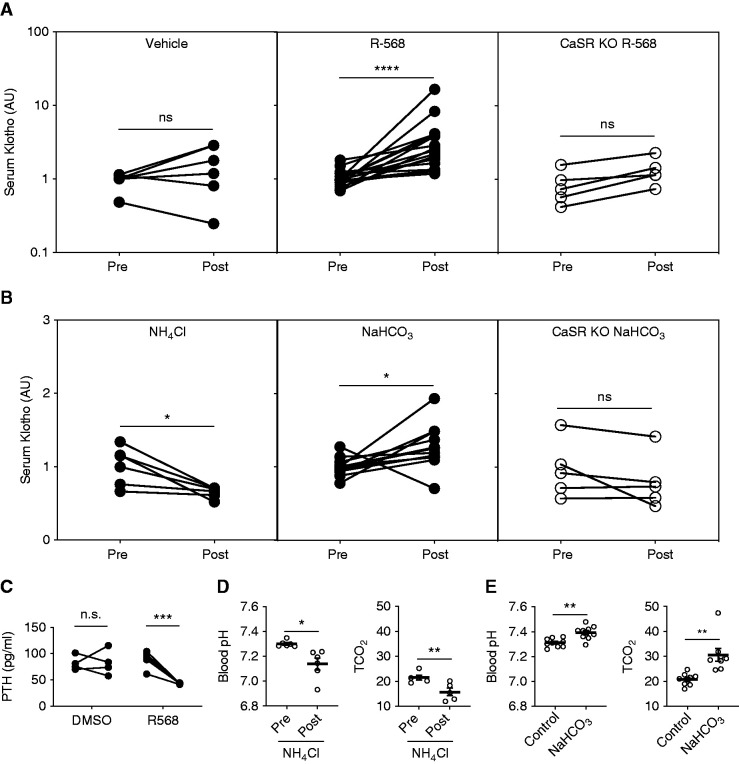
Figure 1.
CaSR activation by a calcimimetic agent or alkaline pH increases soluble αKlotho levels in WT but not TS-CaSR−/− mice. (A) Comparison of serum Klotho before (pre) and 2 hours after (post) treatment with calcimimetic R-568 (0.4 µg/g body wt, IP) or vehicle (equivalent volume of DMSO in saline, IP). R-568 significantly increased serum sKlotho levels (n=12), but fails to do so in response to vehicle (n=6). TS-CaSR−/− (CaSR KO) mice did not significantly respond to R-568 treatment (n=5). The average fold change over pretreatment values are as follows: WT vehicle, 1.6±0.4; WT R-568, 3.6±0.9; CaSR KO R-568, 1.3±0.3. (B) Comparison of serum Klotho before (pre) and 1 hour after (post) administration of 5 μEq/g NH4Cl or 20 μEq/g NaHCO3 (all in water, IP). NH4Cl treatment significantly reduced sKlotho levels (n=6), and HCO3 treatment significantly increased sKotho levels (n=12) in WT mice. The TS-CaSR−/− mice did not respond to HCO3 with an increase in sKlotho (n=5). The average fold change over pretreatment values are as follows: WT NH4Cl, 0.65±0.03; WT NaHCO3, 1.27±0.08; CaSR KO NaHCO3, 0.80±0.16. All serum Klotho values were normalized to the average WT “pre” values on each experimental day. Significance was determined by paired nonparametric, two-tailed t tests, using GraphPad. (C) Plasma PTH is reduced in response to treatment R-568 (n=5), but not DMSO vehicle (n=4). The average PTH levels 30 minutes after treatment were as follows: DMSO, 88.9±7.4 pg/ml; R-568, 43.0±0.55 pg/ml. (D) Blood pH and TCO2 response to NH4Cl (5 mEq/kg body wt, IP). NH4Cl decreased blood pH from 7.30±0.01 to 7.12±0.05, and decreased calculated TCO2 from 21.5±1.0 to 15.7±1.5 mM. (E) Blood pH and TCO2 response to NaHCO3 (20 mEq/kg body wt, IP). NaHCO3 increased blood pH compared with sodium chloride, from 7.32±0.01 to 7.41±0.02, and increased blood TCO2 from 20.8±0.9 to 30.6±2.5 mM. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001, by paired t test in (A), and by t test in (B–E).