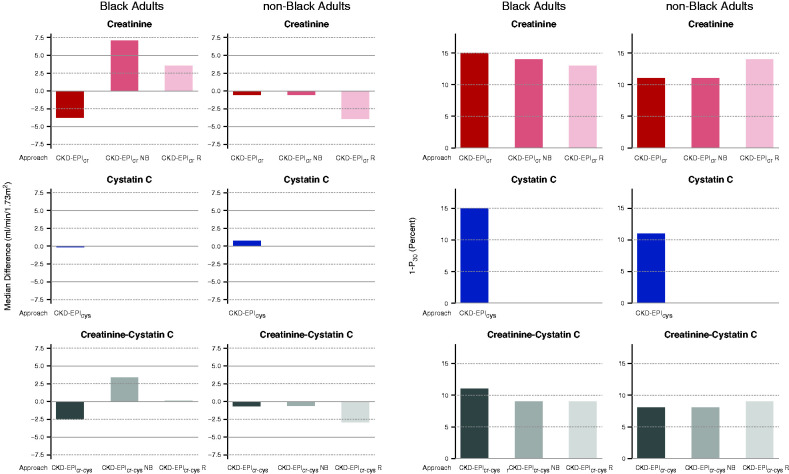
Figure 2.
Performance of approaches CKD-EPIcr, CKD-EPIcr_NB, CKD-EPIcr_R, CKD-EPIcr-cys, CKD-EPIcr-cys_NB, CKD-EPIcr-cys_R, and CKD-EPIcys compared was examined with mGFR for Black and non-Black adults. (Left six panels) Bias as shown as median difference between mGFR and eGFR. Units are milliliters per minute per 1.73 m2. A positive number indicates underestimate of mGFR and a negative number indicates overestimate of mGFR. Solid gray line is the line of identity. Dashed gray lines are drawn at the median difference of 5 and −5 ml/min per 1.73 m2, which is defined as a small bias (shown in Table 2). (Right six panels) Accuracy as shown as percentage of estimates >30% of mGFR (1−P30). Dashed gray lines are drawn at 1−P30 of 10%, which is the definition of small inaccuracy (greatest accuracy), as shown in Table 2. For all panels, the left column shows results for Black adults and the right column shows results as modified from Inker et al.38