Table 1.
Structure, mechanism of action and side effects of NMD pathway inhibitors
| Molecule | Structure | Mechanism of action | Side effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aminoglycosides [71] |
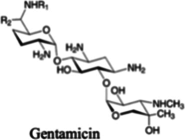
|
PTC readthrough | Toxic at clinical active concentrations |
| Caffeine [72] |
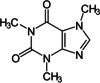
|
SMG1 inhibition | Toxicity, highly aspecific by targeting several kinases |
| NMDI-1 [73, 74] |
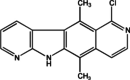
|
Stabilization of the phosphorylated form of UPF1 | No side effects in mice |
| 5-azacytidine [75] |
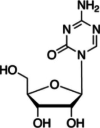
|
Non identified, but c-MYC-mediated | Already approved for the treatment of diverse malignancies |
| Amlexanox [76] |
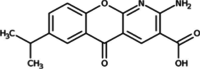
|
Inhibits NMD at a late stage | Clinically approved for aphthous ulcers |
| NMDI14 [77] |
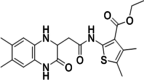
|
Disrupts the SMG7–UPF1 complex | Negligible toxicity in cell-based assays |
