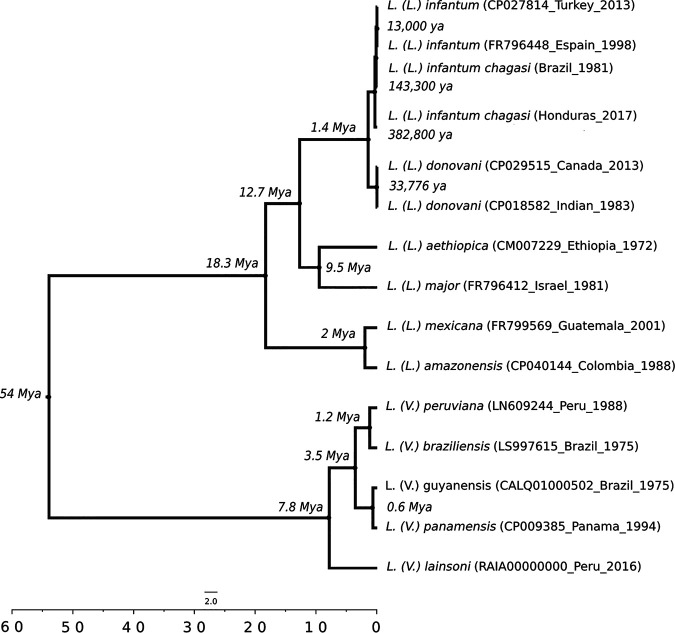
FIG 1.
Bayesian divergence-time analysis under the relaxed molecular clock model for Leishmania species from the Leishmania and Viannia subgenera, using the concatenated data set for the DNA polymerase alpha subunit gene. The x axis shows absolute time in millions of years, and nodes are located at the mean divergence. The molecular clock analysis shows that New World Leishmania infantum chagasi isolates (Brazil_1981 [SRA accession number SRR8842312] and Honduras_2017 [SRA accession number SRR8608748]) experienced divergence ∼143,300 years ago (ya) and ∼382,800 years ago, respectively, and thus are more ancestral than L. infantum isolates from the Old World (Turkey_2013 and Espain_1998), with divergence ∼13,000 years ago. All nodes on the tree are supported with a posterior probability of 1.