Figure 5.
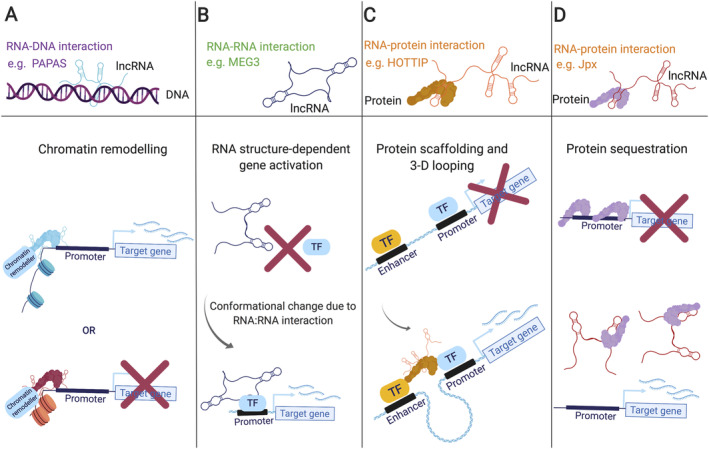
Molecular functions of nuclear lncRNAs. (A) lncRNAs can guide chromatin remodelling complexes to transcription sites, which can either deposit active or repressive chromatin marks (e.g. Xist). (B) lncRNA:RNA interactions can cause a shift in tertiary structure, activating transcription factors which regulate gene expression (e.g. MEG3). (C) By bridging protein interactions or scaffolding the assembly of multi‐protein complexes, lncRNAs can facilitate enhancer and promoter element interactions, critical for gene activation (e.g. HOTTIP). (D) IncRNAs bind specific proteins with high affinity to titrate proteins away from typical occupancy sites, impacting gene activity and/or 3‐D genome compaction (e.g. Jpx). Created using BioRender.
