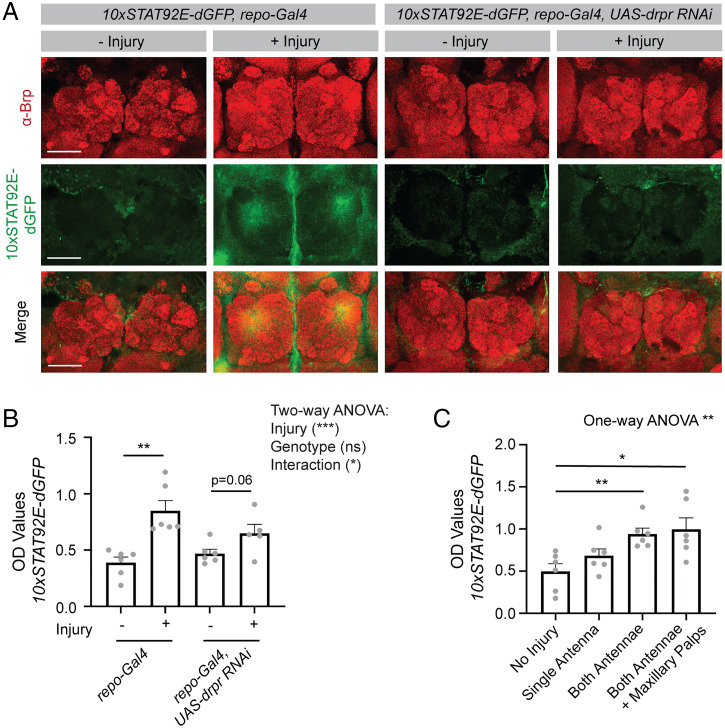
Fig. 3.
The ELISA can be used to screen for transcriptional regulators using GFP transcriptional reporters. The STAT92E-dGFP reporter was expressed ubiquitously and gene expression manipulated in all glia using the repo-Gal4 driver. (A) Both antennae were removed from flies at 9 to 11 dpe and their brains were dissected after 24 ± 2 h. Brains were stained for Brp to label the neuropil and GFP to identify reporter activity. Images were acquired at 20x and a maximum projection of z sections, taken 1 μm apart through the antennal lobes, is shown. (B) Flies were injured as described in A and three fly heads were collected for each sample 24 h after injury. Lysates were prepared, and GFP OD values assessed by ELISA. Statistical comparisons were performed between uninjured (−) and injured (+) flies for each genotype using a two-way ANOVA, and unpaired two-sided t tests were performed between injury conditions within each genotype (repo-Gal4 – injury n = 6, repo-Gal4 + injury n = 6, repo-Gal4 UAS-drpr RNAi – injury n = 6, repo-Gal4 UAS-drpr RNAi + injury n = 6). (C) Graded severities of injury, as indicated on the x axis, were performed in flies expressing the STAT92E-GFP reporter and GFP OD values were measured by ELISA. A one-way ANOVA was performed across all injury conditions and unpaired, two-sided t tests were performed between the no injury condition and each of the injury conditions (no injury n = 6, single antenna n = 6, both antennae n = 6, antennae + maxillary palps n = 6). Graphs represent mean ± SEM *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, or as indicated. (Scale bar, 50 μm.)