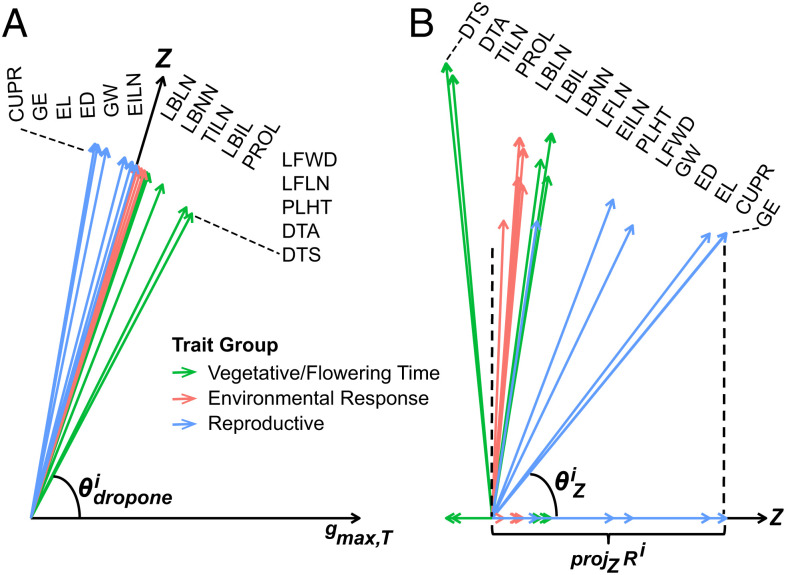
Fig. 6.
Constraints and consequences of multivariate selection. (A) Individual trait contribution toward genetic constraint is identified by dropping the trait from (actual domestication trajectory) and (genetic lines of least resistance) and measuring the angle between the two vectors. If is smaller than = 66.3° (angle between and ), then the trait is said to constrain evolution. If is larger than , then the trait is said to assist evolution. (B) Multivariate response () from hypothetical selection on a single trait. is compared to through the angle (), and scalar projection () of on . measures the deviation from by selecting on the trait. measures the evolutionary gain along by selecting on the trait.