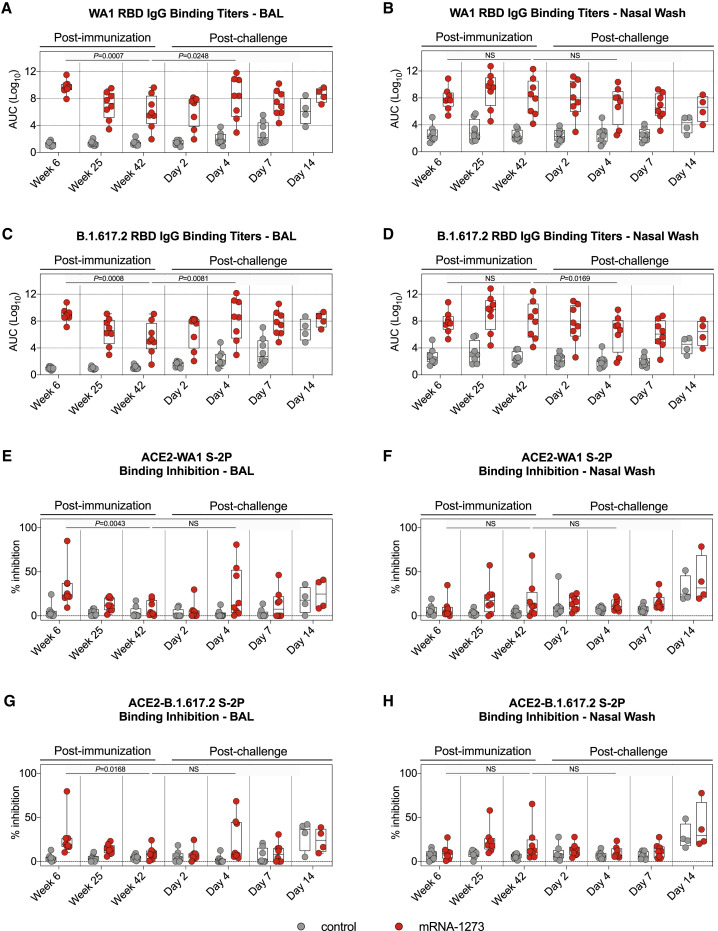
Figure 3.
RBD-binding mucosal antibodies observe distinct kinetic patterns in the upper and lower airways
(A–D) BAL and nasal washes were collected at weeks 6, 25, and 42 post-immunization and days 2, 4, 7, and 14 post-challenge. (A and B) WA1 and (C and D) B.1.617.2 RBD-binding IgG titers in the lower (A and C) or upper (B and D) airways. Circles in (A)–(D) indicate individual NHPs. Boxes represent interquartile range with the median denoted by a horizontal line. Dotted lines are for visualization purposes and denote 4-log10 increases in binding titers. 4–8 NHPs per group.
(E–H) BAL and nasal washes were collected at weeks 6, 25, and 42 post-immunization and days 2, 4, 7, and 14 post-challenge. All samples diluted 1:5. SARS-CoV-2 WA1 (E and F) and B.1.617.2 (G and H) S-2P binding to ACE2 measured both alone and in the presence of BAL (E and G) or nasal wash (F and H) in order to calculate the percentage of inhibition. Circles denote individual NHPs. Boxes represent interquartile range with the median denoted by a horizontal line. Dotted lines set to 0% inhibition. 4–8 NHPs per group.
Statistical analysis in (A)–(H) shown for mRNA-1273 cohort only.