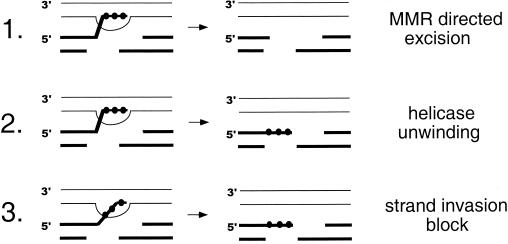
FIG. 2.
Models to explain rejection of heteroduplex intermediates containing mispairs via MMR proteins. In this figure, base pair differences between the recipient and donor chromosomes are indicated by the solid circles. (1) The mismatch correction process itself could lead to resection of nicked strands and the creation of a single-stranded gap that destroys the recombination intermediate. (2) hDNA rejection results in the unwinding of the annealed strands by a helicase that takes its cue from interactions with bound Msh factors. (3) Binding of MMR factors blocks attempted hDNA formation (Sugawara et al., unpublished).