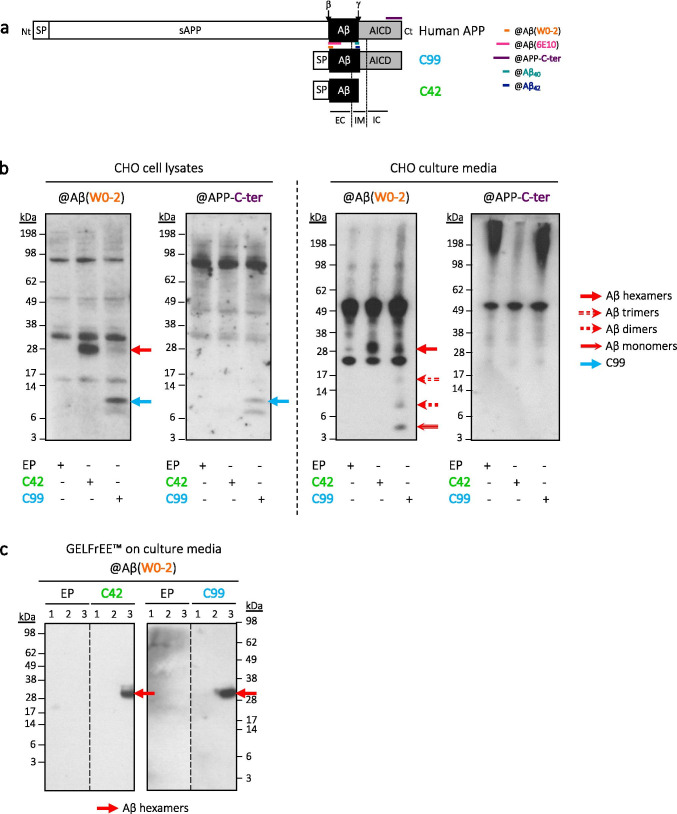
Fig. 1.
Hexameric Aβ42 derived from CHO cells expressing human APP metabolites. a Full-length APP is cleaved by β-secretase at the β site, located at the N-terminus of Aβ, to produce a 99-amino acid membrane-bound fragment (C99) encompassing Aβ and AICD. The C99 construct expressed here in the cells was fused to the signal peptide (SP) of APP. C99 is cleaved by γ-secretase to release Aβ. The C42 construct is composed of the SP of APP and the Aβ42 sequence. The epitopes of the primary antibodies used in this study are indicated on the scheme; either directed against human Aβ (clones W0-2 and 6E10 targeting its N-terminal part, and Aβ40 and Aβ42 antibodies specifically targeting the free C-terminal end of Aβ) or against the C-terminal region of APP (APP-C-ter). Nt N-terminus, Ct C-terminus, sAPP soluble APP, AICD APP intracellular domain, EC extracellular, IM intramembrane, IC intracellular. b Detection of ~ 28 kDa assemblies by Western blotting in CHO cell lysates and culture media following expression of either C42 or C99. These assemblies are recognized by Aβ specific antibodies (such as W0-2 here), but not by the anti-APP-C-ter, suggesting they emerge by assembly of Aβ. Media samples were lyophilized and all samples were immunoprecipitated with the anti-Aβ (W0-2) antibody prior to analysis. In the media of C99-expressing cells, intermediate assemblies are also observed; monomers, dimers, and trimers. EP empty plasmid. c Isolation of cell-derived Aβ assemblies. The media of CHO cells expressing either EP, C42, or C99 were immunoprecipitated and separated using the GELFrEE™ technique. We optimized a method to collect the ~ 28 kDa Aβ assemblies as an isolated liquid fraction. Dashed lines indicate that proteins were run on the same gel, but lanes are not contiguous