FIG. 3.
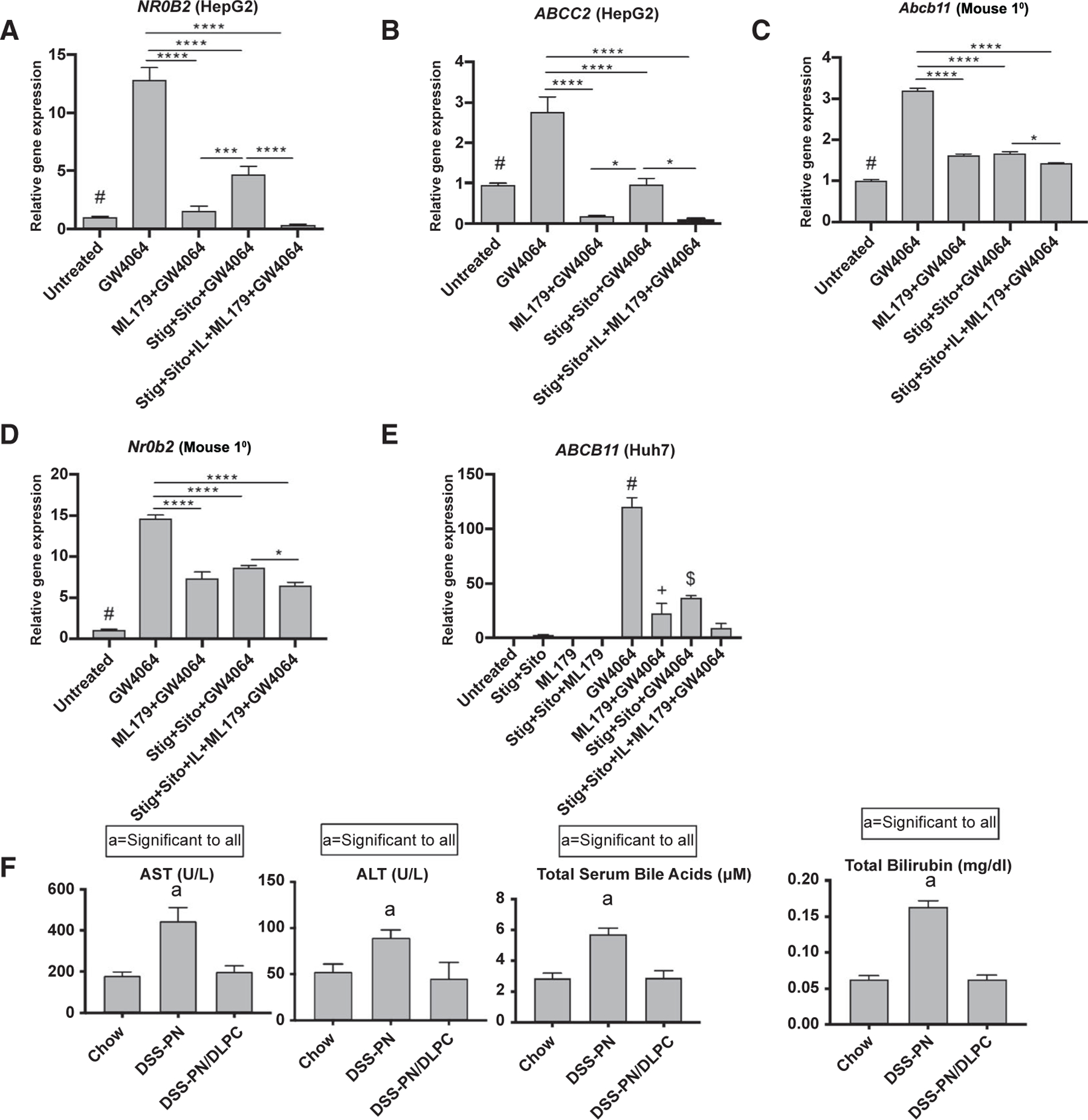
Effect of inhibition of LRH-1 on FXR target genes in cultured cells and of LRH1 agonist treatment in DSS-PN mice. Cultured cells were incubated with LRH-1 inverse agonist ML179 for 4 hours followed by addition of GW4064 +/− stig+sito overnight, and mRNA expression was then analyzed. (A) NR0B2/SHP in HepG2 cells. #P < 0.0001 versus GW4064 and GW4064 + stig+sito. (B) ABCC2/MRP2 in HepG2 cells. #P < 0.05 versus all groups except stig+sito + GW4064. (C) Abcb11/BSEP in primary mouse hepatocytes (Mouse 1°). #P < 0.0001 versus GW4064 group. (D) Nr0b2/SHP in primary mouse hepatocytes. #P < 0.0001 versus all other groups. (E) ABCB11/BSEP in Huh7 cells. #P < 0.0001 versus all other groups. *P < 0.05 versus all groups except stig+sito + GW4064. $P < 0.01 versus all groups except ML179 + GW4064. Gene expression was normalized to HPRT1/Hprt1. (F) Serum AST, ALT, total serum bile acids, and total bilirubin in chow, DSS-PN, and DSS-PN /DLPC (LRH1 agonist)–treated mice. Statistical analysis was performed by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s correction for multiple comparisons. *P < 0.05 and ****P < 0.0001.
