Figure 1: Method of antibody-nanoparticle conjugate (ANC) formation.
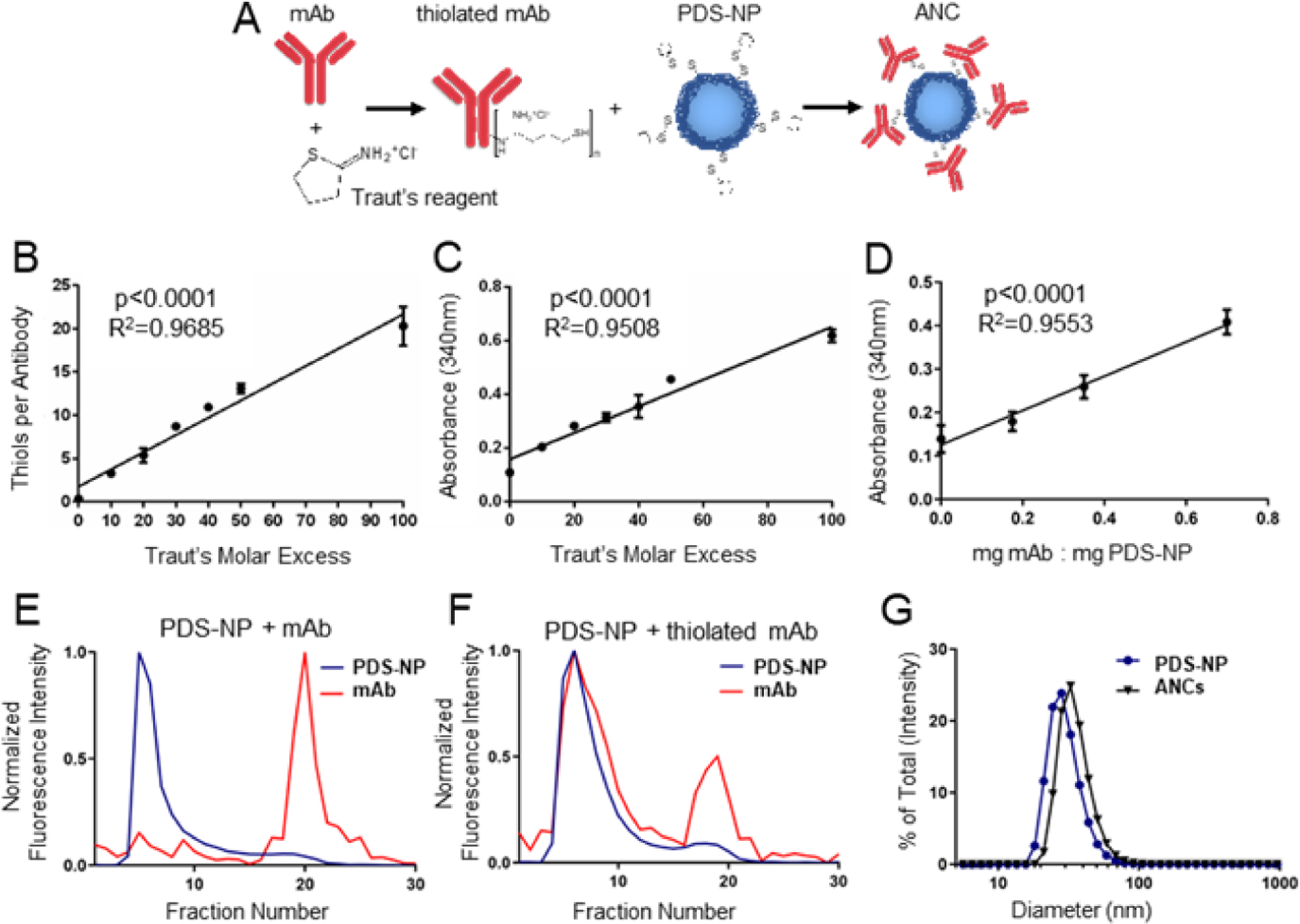
A) Schema of ANC formation wherein monoclonal IgG antibody (mAb) that is thiolated using Traut’s reagent is mixed with pyridyl disulfide (PDS)-derivatized PPS-NP (PDS-NP) to result in conjugation of mAb to PPS-NP via a disfulide linkage. The molar excess of Traut’s reagent controls number of thiols per mAb, as measured by Ellman’s assay (B), and extent of mAb conjugation to PDS-NP, as measured by 340 nm absorbance of the released pyridyl at 340 nm (C). D) Loading ratio of thiolated mAb to PDS-NP additionally controls the extent of mAb conjugation to PDS-NP, as measured by 340 nm absorbance of released pyridyl. Intensity of fluorescently labeled mAb or PDS-NP in eluted fractions from size exclusion chromatography when mAb was left unmodified (E) or thiolated using Traut’s reagent (F). G) Dynamic light scattering plots of plain NPs and ANCs post size exclusion purification and concentration. Statistical analyses were done using linear regression.
