Figure 5: ICB-ANCs target NP-encapsulated small molecules to immune checkpoint-expressing cells in vitro.
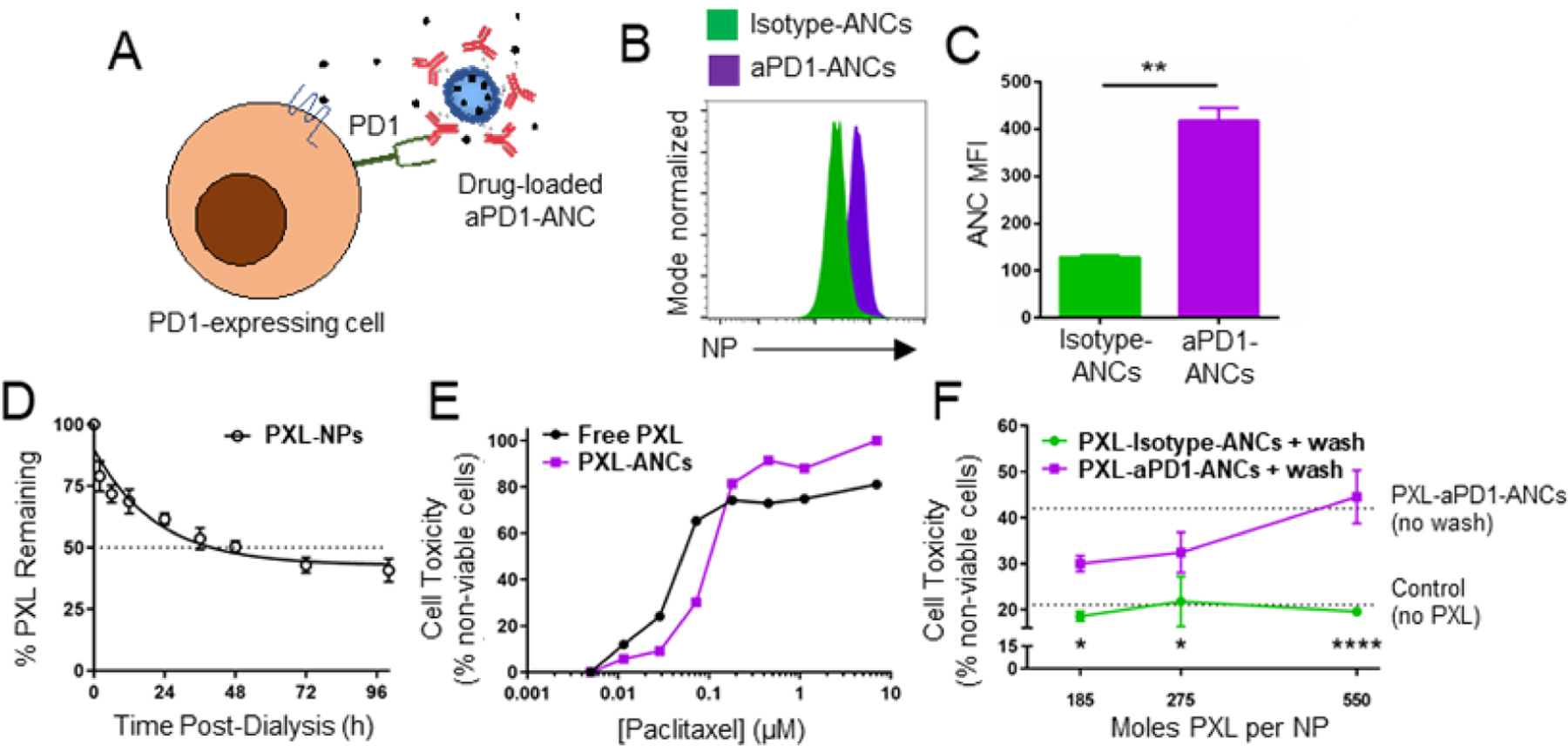
A) Schematic of ICB-ANC-mediated co-delivery of small molecule drugs to immune checkpoint-expressing T cells. Histogram (B) and MFI (C) of flow cytometrically measured NP signal of fluorescently labeled (AlexaFluor647) NPs from isotype- or aPD1-ANCs after 15 min co-incubation in vitro with PD1-expressing EL4 cells and serial washing. D) Fraction of initial loaded paclitaxel (PXL) amount remaining in NP during in vitro release with dialysis. E) Fraction of plated EL4 cells non-viable after 72 h treatment with free or NP-encapsulated PXL. F) aPD1 targeting improves cytotoxic effects of PXL-loaded ANCs on PD1-expressing EL4 cells. Cells were co-incubated in vitro with PXL encapsulated within isotype- or aPD1-ANCs for 15 min followed by two washes and subsequently cultured in drug- and NP-free media for 72 h. Controls include untreated cells or cells treated with ANCs without washing (dotted lines). Statistical analyses were done using two-tailed unpaired t-test (C) or two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s test (F). *p<0.05, **p < 0.01, ****p < 0.0001.
