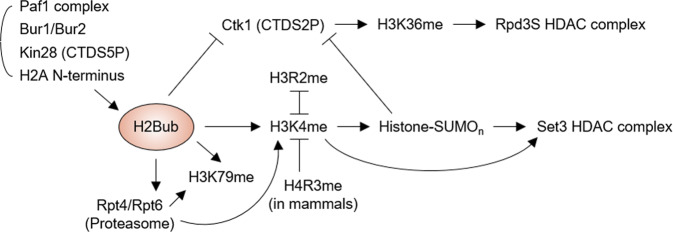
Fig. 1. H2B monoubiquitination-centered crosstalk pathway in S. cerevisiae.
The Paf1 complex, Bur1/Bur2 and Kin28 kinases, and N-terminal tails of H2A facilitate H2B monoubiquitination (ub) during yeast transcription. H2Bub then promotes H3K4 and H3K79 methylation (me) both directly and via the proteasomal ATPases Rpt4 and Rpt6. H3R2me mutually antagonizes H3K4me, whereas H4R3me interferes with the binding ability of H3K4 methyltransferase (no reports of H4R3me in S. cerevisiae). Although either H2Bub- or H3K4me-stimulated histone (poly)sumoylation blocks the recruitment of Ctk1 CTDS2 kinase, facilitating H3K36me modification for loading of the Rpd3S HDAC complex, both H3K4me and histone (poly)sumoylation are required for the chromatin binding of the Set3 HDAC complex.