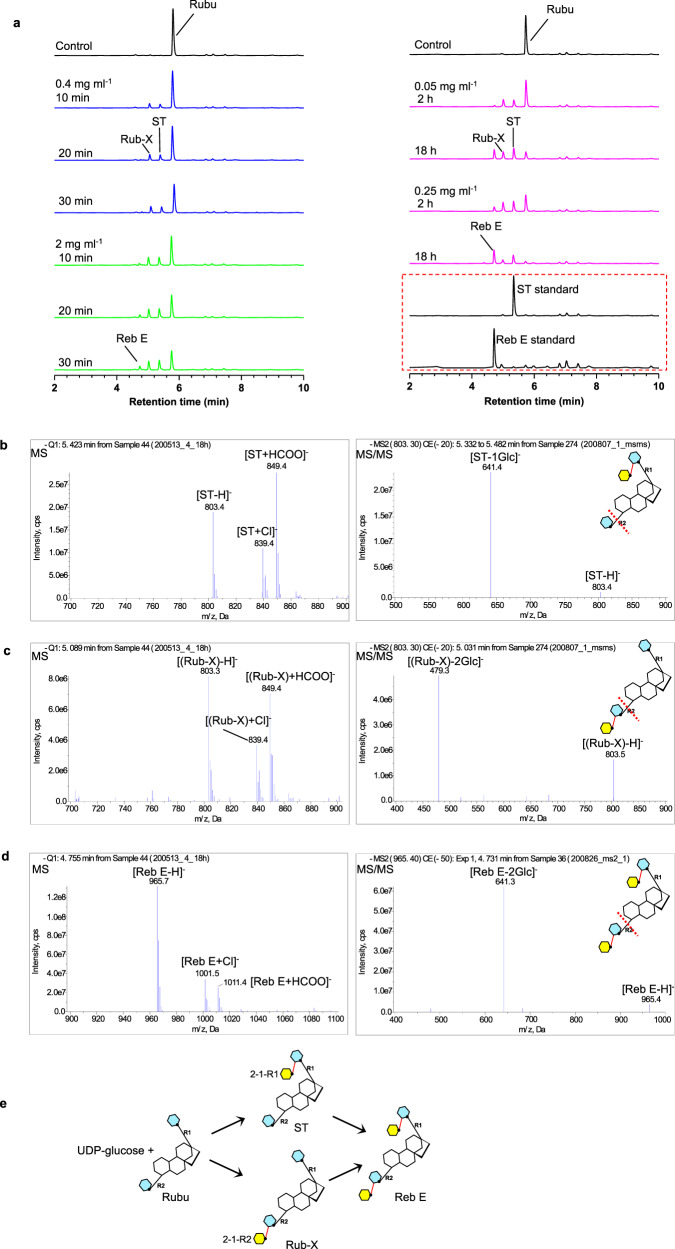
Fig. 2. β (1–2) sugar transfers by OsUGT91C1 at both the R1 and R2 ends of Rubu.
a LC-MS was used to monitor the reaction of Rubu with OsUGT91C1 and UDP-glucose. The HPLC traces represent the 18 h control reaction without the enzyme (black); the incubations for 10 min, 20 min, and 30 min with the enzyme at 0.4 mg ml−1 (blue); the incubations were repeated with the enzyme (5x) at 2.0 mg ml-1 (green). The HPLC traces in pink report the incubation with the enzyme at 0.05 mg ml-1 for 2 h and 18 h, repeated with 0.25 mg ml−1 enzyme (5x). The authentic standards ST and Reb E are shown in the red dashed box. b–d Mass spectra of the three new peaks in LC-MS are consistent with the assignment of ST (b), Rub-X (c), and Reb E (d). The main negative derived ions of the products ST, Rub-X, and Reb E are labeled in MS analyses. The negative parent ions [ST-H]−, [(Rub-X)-H]−, and [Reb E-H]− with m/z at 803, 803, and 965 were explicitly isolated and then characterized by MS/MS, where the more labile ester bond breaks first in MS/MS, leading to the first mass loss of ester-linked glycan at the R2 end from the parent ion. The size of the mass loss of the abundant fragment ions of ST, Rub-X, and Reb E indicates the number of ester-linked glucose units at the R2 end. The insert denotes where the ester bond breaks first during MS/MS fragmentation with a red dash line. e Cartoon of the reactions catalyzed by OsUGT91C1 on Rubu.