Extended Data Figure 4 |. ALK binding and signaling by ALKAL2-AD.
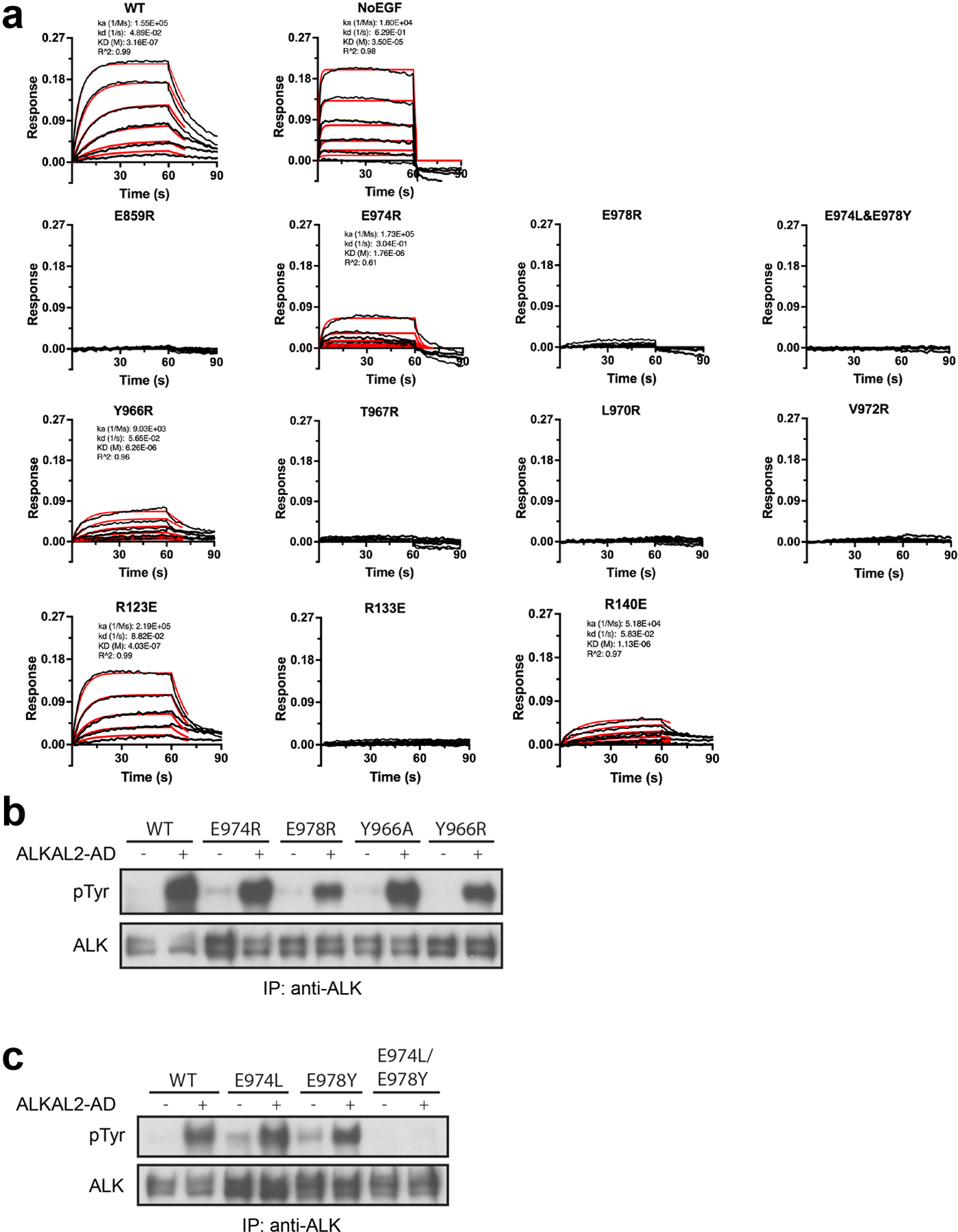
a, Representative BLI sensograms traces (black) and kinetic fittings (red). Fitting was carried out using ForteBio Data Analysis 10.0 software using 1:1 model with Rmax linked global fitting. Where appropriate, kinetic fit parameters are included. b-c, NIH 3T3 cells stably expressing wild type (WT) or mutated full length ALK, stimulated with high concentrations (10 nM) of ALKAL2 to assess residual signaling ability. b, Single point mutations of conserved binding-site residues. E978R has the greatest impact on ALKAL induced ALK signaling in agreement with binding data. c, C-terminal conserved glutamates mutated to the residues found at the same position in invertebrate ALK. The double (E974L/E978Y) mutant fails to signal, consistent with it being the only mutation shown here that completely abolished ligand binding in (a) (Extended Data Table 3). For gel source data, see Supplementary Figure 2. The stimulation experiment was repeated three times with similar results.
