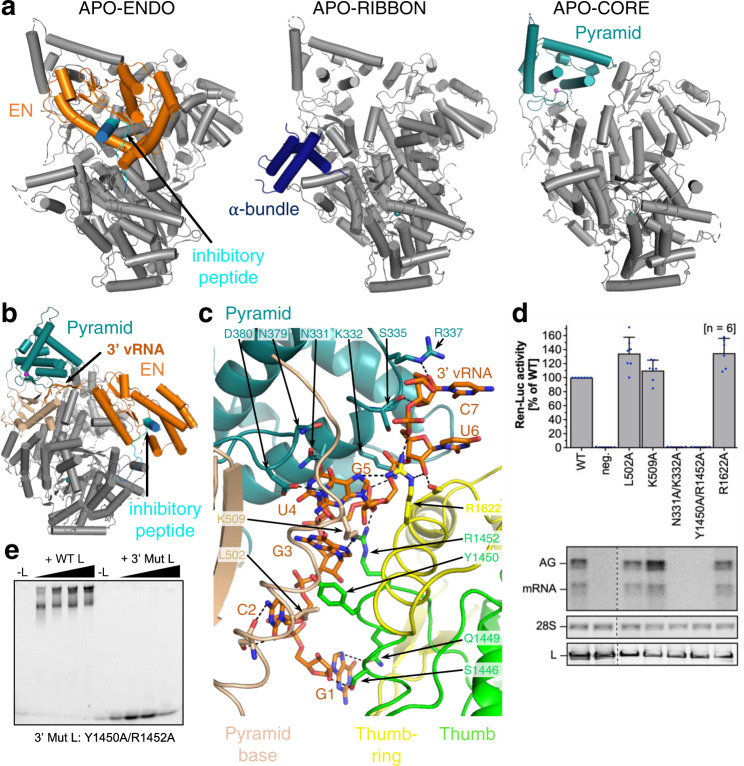
Fig. 1. L protein in the apo-state and with 3′ viral RNA bound in the secondary binding site.
a Ribbon diagram presentations of the structures APO-ENDO, APO-RIBBON and APO-CORE. Each of the respective experimental maps resolves distinct regions of the L protein better than the others and those regions are shown in colour and indicated by name in the respective structures. b Overall structure of L protein 3END-CORE as a ribbon diagram with the 3′ vRNA bound below the pyramid domain. Pyramid (teal), pyramid base (wheat), EN domain (orange) and the inhibitory peptide (cyan) are highlighted. c Close-up of the secondary 3′ vRNA binding site with the 3′ vRNA nucleotides 1–7 (orange), pyramid domain (teal), pyramid base (wheat) as well as thumb (green) and thumb-ring (yellow) domains. Important amino acids in the RNA-protein interface are shown as sticks with respective labels. Hydrogen bonds are indicated by dotted lines. For selected regions, secondary structure depiction was disabled to enhance visibility. d LASV mini-replicon data for L proteins with mutations in the secondary 3′ RNA binding site presenting luciferase reporter activity (in standardised relative light units relative to the wild-type L protein (WT)). Data were presented as mean values ± SD of at least six biological replicates (n = 6), although for most mutants seven biological replicates were included. All biological replicates are shown as blue dots (top panel). Middle panels present Northern blotting results with signals for antigenomic viral RNA (AG), viral mRNA (mRNA) and 28 S ribosomal RNA (28 S) as a loading control, and the bottom panel shows Western blot detection of FLAG-tagged L proteins (L) to demonstrate general expressibility of the mutants. Source data are provided in a Source Data file. e Electrophoretic mobility shift assay of wild-type L protein (WT L) and mutant Y1450A/R1452A (Mut L) with 10 nt 3′ viral RNA. L protein concentrations ranging from 0–1 µM and 0.2 µM of fluorescently labelled 3′ vRNA (Supplementary Table 1) were used (see methods).