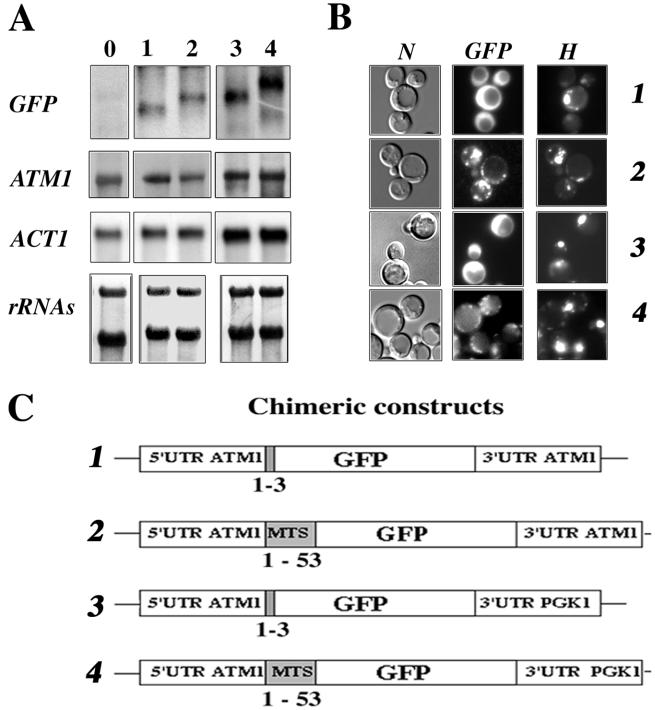
FIG. 3.
Expression and localization of GFP-Atm1p chimeras. (A) A portion (30 μg) of RNA prepared from whole cells was separated on formaldehyde-agarose gels and subjected to Northern blot analysis using specific radiolabeled probes. Lane 0 represents CW04 wild-type cells devoid of recombinant plasmids, and lanes 1 to 4 represent CW04 cells expressing plasmids 1 to 4, respectively, shown in panel C. The approximate sizes of each individual GFP hybrid mRNA were as follows: plasmid 1, 0.75 kb; plasmid 2, 0.9 kb; plasmid 3, 0.9 kb; and plasmid 4, 1.1 kb. (B) Direct fluorescence microscopy of CW04 cells carrying plasmids expressing the GFP chimeras. Panel N represents the cells viewed by Nomarski optics, panel GFP represents the GFP signal, and panel H shows cells stained with the DNA dye reagent Hoechst. Cells carrying plasmids 1 and 3 had homogeneous cytosolic staining, in contrast to cells carrying plasmids 2 and 4, which gave a cytoplasmic GFP signal localized to discrete spots, which were also stained by the DNA reagent Hoechst. (C) Representation of the four chimeric constructs tested. GFP protein is expressed under the control of ATM1 promoter. All of the plasmids shared the complete 5′UTR of ATM1, and translation for all them was initiated at the authentic Atm1p AUG. For plasmids 1 and 3, the GFP AUG is in the fourth position of the chimeras. In contrast, fusion proteins translated from plasmids 2 and 4 possess the entire Atm1p 53-amino-acid presequence in frame with the GFP AUG codon. In plasmids 3 and 4, the 3′UTR of ATM1 was replaced with the 3′UTR of PGK1, a gene coding for a cytoplasmic protein and usually used as a marker of soluble cytosolic fractions (52).