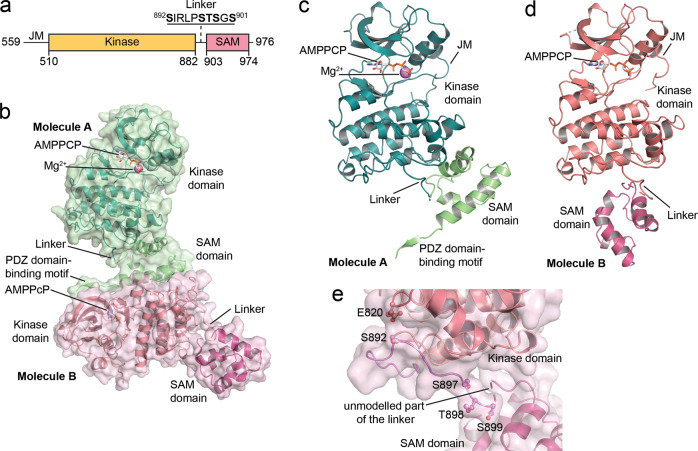
Fig. 1. Crystal structure of the EphA2 wild-type intracellular region.
a Schematic illustrating the domains of the EphA2 intracellular region. b Overview of the two EphA2 molecules in the crystallographic asymmetric unit; resolution 1.75 Å. Molecule A is shown in green, with the kinase domain in darker green and the SAM domain and C-terminal tail in lighter green. The kinase and SAM domains of molecule B are shown in two different shades of red. The ATP-analog β,γ-methyleneadenosine 5′-triphosphate (AMPPCP), present in the active sites of both molecules A and B, is shown as gray sticks and a Mg2+-ion in the active site of molecule A is shown as a purple sphere. The kinase domains in both molecules adopt the active DFG-in conformation. The regions that are well defined in both EphA2 molecules include the portion of the juxtamembrane segment encoded by our construct, most of the kinase domain, and the whole SAM domain. Parts of the activation loop (L760-I779), residues S636-G637 in the short β1-2 loop of the N-lobe of EphA2 molecule B, and parts of the kinase-SAM linker (S899-V904 in molecule A and G900-V904 in molecule B) are not defined due to lack of electron density. The C-terminal tail (K966-I976) including the PDZ domain-binding motif is defined only in molecule A. c Rotated view of molecule A, highlighting the compact arrangement of the kinase and SAM domains. Missing portions of the linker in c and d are shown as a dashed line. d Rotated view of molecule B, with the kinase domain in the same orientation as for molecule A in panel c. The kinase and SAM domains are in a less compact arrangement. e Detail of the kinase-SAM linker of molecule B, showing that the S892, S897, T898, and S899 phosphorylation sites are solvent exposed and accessible. The fifth phosphorylation site (S901) is in the undefined region of the linker, which is indicated by a dashed connector. E820 is in close proximity (3–5 Å) to S892 and might be an allosteric sensor of linker phosphorylation.