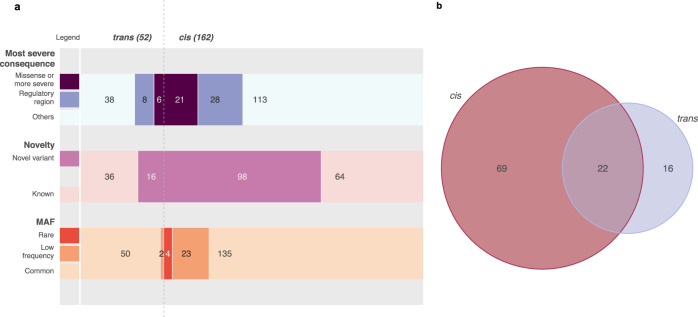
Fig. 2. Overall genetic architecture of 107 serum proteins of neurological relevance.
a A total of 214 independent variants were detected. Cis-acting variants were defined as variants lying within 1 Mb upstream and downstream of the gene encoding the target protein, while trans-acting variants are variants that lie outside of this region. Most severe consequence was determined by Ensembl’s variant effect predictor (VEP). Effects more than missense included ‘stop_gained’, ‘frameshift_variant’, and ‘splice_acceptor_variant’ in our dataset; ‘Regulatory region’ variants include ‘[3/5]_primeUTR_variant’, ‘TF_binding_site_variant’, ‘splice_region_variant’, and ‘regulatory_region_variant’; while’Others’ comprises mostly intergenic and intronic variants. Novelty was assessed by cross-referencing published summary statistics from other pQTL studies (Supplementary Data 2). Known pleiotropic loci were not considered novel. Rare, low-frequency and common variants were defined as variants with minor allele frequency (MAF) < 1%, MAF 1–5%, and MAF > 5%, respectively. b Number of proteins for which we detected only cis-pQTLs, trans-pQTLs, or both.