Fig. 5. Associations of the top RNA editing events with AD risk and pathologies.
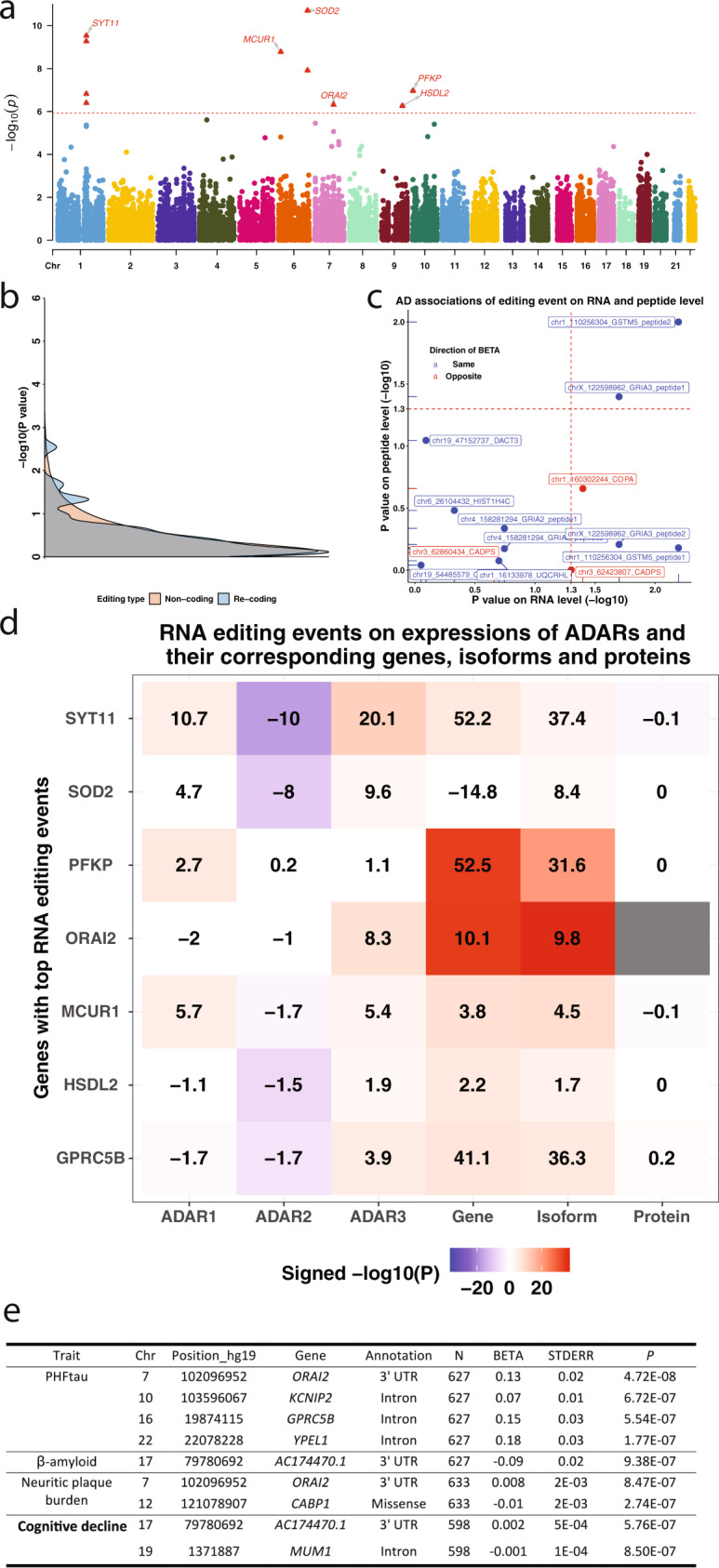
a Manhattan plot of the Stage II association analysis of RNA editing with clinical status of AD. Each dot represents one RNA editing event, and the X and Y axes show its genomic coordinate and −log10 transformed meta-analyzed P value. The horizontal red dashed line shows the Bonferroni-corrected genome-wide significance threshold (P ≤ 1.2 × 10−6) and those passing the threshold were shown as the red triangles with gene names. b The density plots showed the comparisons of the AD association P values (−log10) of the non-coding (orange) and re-coding events (blue). c Scatter plot showed the P values (−log10) of the associations of the re-coding event with Alzheimer’s disease based on both the RNA-seq (X axis) and proteomic dataset (Y axis). Blue dot and font represent those events with regression coefficients in the same direction (RNA-seq vs. peptide analysis), while the red dot and font represent those events with regression coefficients in the opposite direction. d The matrix plot shows the associations of the top RNA editing events with expressions of ADARs and the mRNA and protein expressions of the gene harboring the editing event. The transformed BETA values (times 100) of effect of RNA editing level (% editing) on the outcomes are presented. The signed −log10(P) values were coded for different colors where white was for values between −1.3 and 1.3 (P = 0.05), darkening blue was for negative values from 0, and darkening red was for positive values from 0. e Top RNA editing events associated with AD pathologies in Stage I samples. BETA, STDERR, and P represent the regression coefficient, standard error, and corresponding P values of the generalized linear model of RNA editing level (% alternative allele) as the exposure and each of the trait as the outcomes. The displayed P values were not adjusted by the multiple testings and were derived by two-sided tests.
