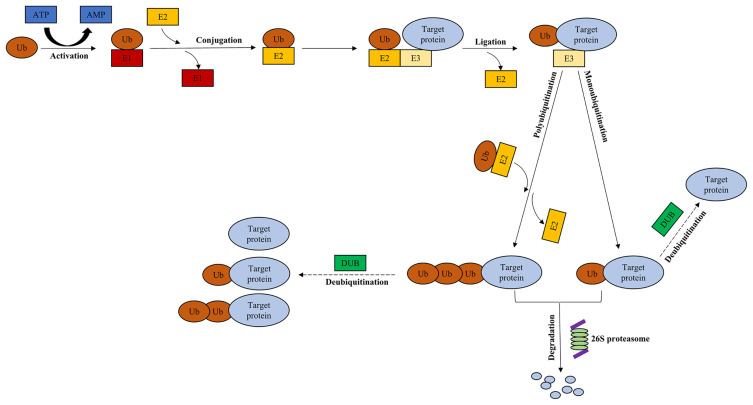
Figure 1.
Ubiquitin-proteasome system. Ubiquitination of the target protein is catalyzed through E1, E2, and E3. Ub is activated by E1 in an ATP-dependent manner, which is subsequently transferred to E2. Then, an isopeptide bond is formed following the conjugation between ubiquitin and a lysine residue of the target protein via E3. Finally, the target protein is recognized by 26S proteasome, leading to the degradation of protein. The presence of DUBs rescues the target protein from being degraded, and contributes to its stabilization through deubiquitination. Dotted arrow: deubiquitination. Ub, ubiquitin; E1, ubiquitin‐activating enzyme; E2, ubiquitin‐conjugating enzyme; E3, ubiquitin ligase enzyme; DUB, deubiquitinating enzyme.