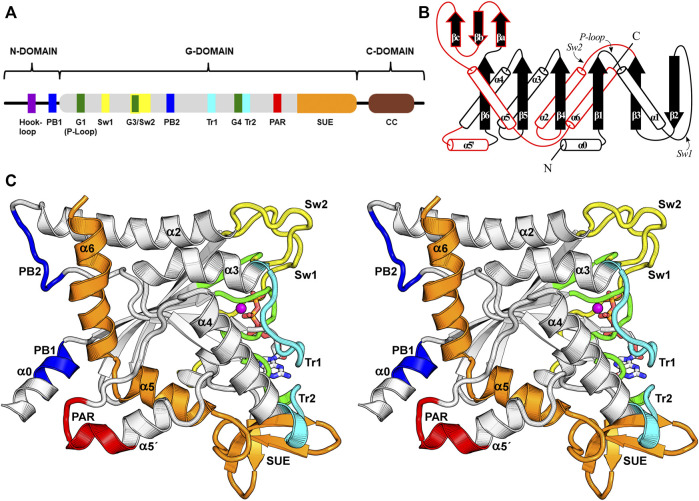
FIGURE 3.
The septin G-domain. (A) Schematic representation of the septin domains and their hallmark features. The N-domain presents variable length and encompasses the α0 helix, which contains the polybasic region 1 (PB1). The G-domain contains all the essential nucleotide-binding motifs (G1, G3, G4) and the switches important for catalysis. Other functional elements related to interface formation, such as a second polybasic region (PB2), a polyacidic region (PAR), the trans-loops 1 and 2 (Tr1 and Tr2) and the septin unique element (SUE) are also indicated. The C-domain often contains heptad repeats that form coiled coils (CC). (B) A schematic topology diagram for the septin G-domain fold. Three unique features observed in septins are highlighted in red. (C) Stereo representation of the G-domain highlighting some of its features employing the same color code used in panel (A). Several of these features and secondary structure elements are labeled. The PB1, PB2 and PAR are close to the NC-interface, while the switch I (Sw1), switch II (Sw2), Tr1 and Tr2 participate in the G-interface. The SUE is an exclusive feature of septins and participates in both interfaces. The Mg2+ ion is coloured in magenta.