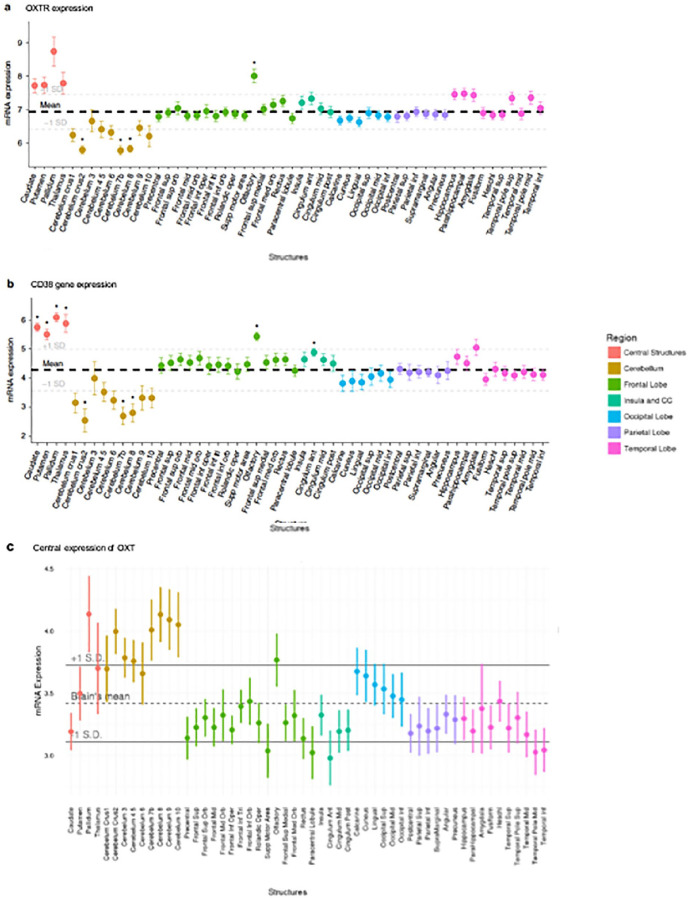
Figure 2.
Oxytocin pathway gene expression in the postmortem human brain. Each point represents the mean expression from six donors collected from the Allen Human Brain Atlas (http://human.brain-map.org/). (a) Expression of OXTR mRNA. Higher than average expressions of OXTR mRNA levels was observed in the olfactory bulbs and several subcortical regions. (b) CD38 gene expression was higher than average in the caudate, pallidum, olfactory bulbs, putamen, thalamus, and cingulate anterior. (c) The central expression of OXT. No brain regions were associated with higher than average OXT expression after FDR correction. The bolded dashed lines represent mean expression across all regions plus 1 standard deviation (+/−). CD38, cluster of differentiation 38; FDR, false discovery rate; mRNA, messenger ribonucleic acid; OXT, oxytocin, OXTR, oxytocin receptor; SD, standard deviation. Material from: Quintana and others (2019). Oxytocin pathway gene networks in the human brain, Nature Communications, published 2019 by Springer Nature under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license.