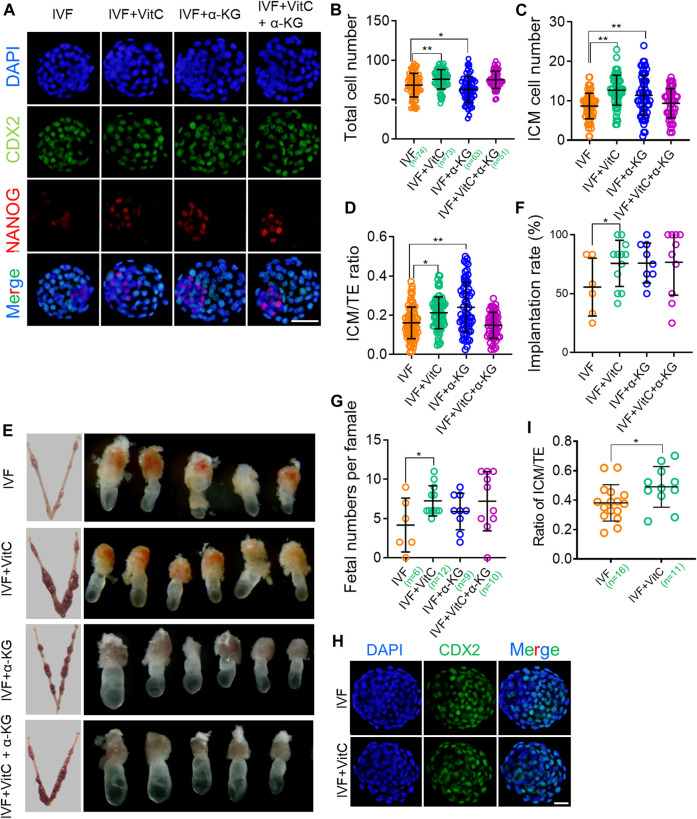
FIGURE 5.
Vitamin C regulates preimplantation lineage differentiation and promotes developmental potential of IVF blastocysts (A) Immunofluorescent images of NANOG and CDX2 in IVF blastocysts incubated with vitamin C or α-KG alone, or in combination. The embryos were counterstained with DAPI (B-D) Effects of supplementation with vitamin C or α-KG alone, or in combination on total cell numbers (B), ICM cell numbers (C), and ratios of ICM/TE (D) in IVF blastocytes. ICM and TE cell numbers were calculated by counting NANOG-positive and CDX2-positive cells. Circles represent cell numbers or ratios in each embryo. The number of embryos in each group is indicated (E) Representative images of the implantation sites (left column) at E7.5 in each group following embryo transfer, and morphological comparison of recovered E7.5 embryos among groups (right column) (F) Quantifications of implantation rates of transferred embryos in each group. Circles represent implantation rate of each female recipient (G) Number of survived embryos with normal morphologies at E7.5 in each group following embryo transfer. Circles represent survived embryo in each female recipient. The number of recipients in each group is indicated (H) Immunofluorescent images of CDX2 in IVF bovine blastocysts incubated with vitamin C (I) Effects of supplementation with vitamin C on ratios of ICM/TE in IVF bovine blastocysts. ICM and TE cell numbers was calculated by counting CDX2-negative and CDX2-positive cells. The number of embryos in each group is indicated. Data show the means ± SD of three independent experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. Scale bar, 50 μm.