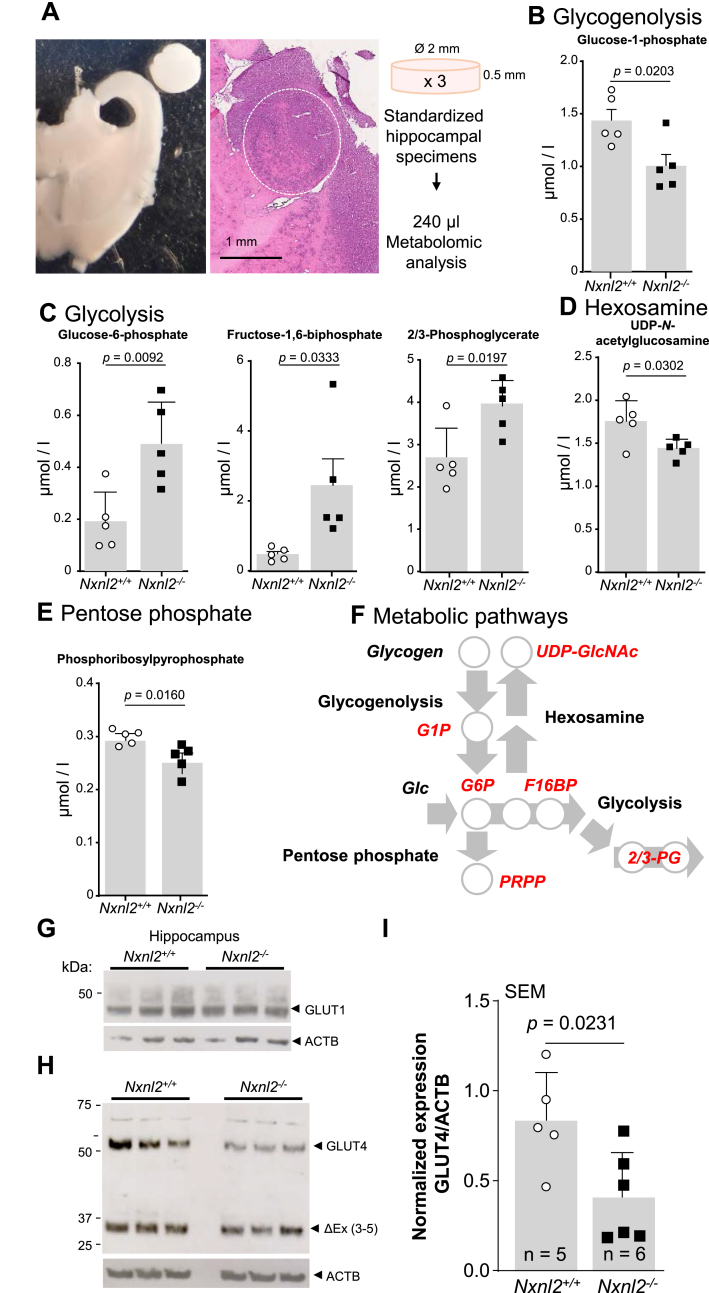
Fig. 4.
Metabolomic analysis of hippocampal standardized specimens of Nxnl2−/− mice. (A) Representative pictures of a standardized specimen of the hippocampus. Left, bright-field microscopy and right hematoxylin and eosin staining. The white dotted circle delineates the surface of the hippocampal specimen. (B–F) Metabolomic analysis of the hippocampus specimens of 2-month ♂ mice. (B) Glycogenolysis. (C) Glycolysis. (D) Hexosamine pathway (E) Pentose phosphate pathway. (F) Metabolic pathways. 2/3-PG: 2/3-phosphoglycerate, F16BP: fructose-1,6-biphosphate, G1P: glucose-1-phosphate, G6P: glucose-6-phosphate, PRPP: phosphoribosylpyrophosphate and UDP-GlcNAc: UDP-N- acetylglucosamine. (G) Expression GLUT1 (SLC2A1) in the hippocampus specimens of 2-months ♂ mice. (H) Expression GLUT4 (SLC2A4) in the hippocampus specimens of 2-months ♂ mice. The invariant band ΔEx (3–5) is most likely a splicing variant previously reported. I) Quantification of the expression of GLUT4 in the hippocampus specimens of 2-months ♂ mice. The data are plotted with SEM. The data were analyzed by t-tests using GraphPad.