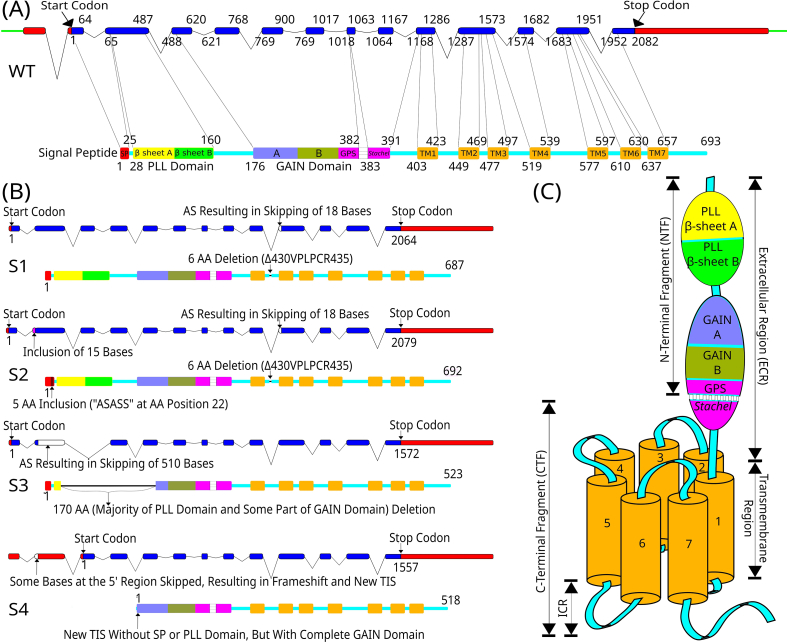
Fig. 1.
Organization of the GPR56 gene and receptor protein variants. (A) Schematic diagrams of the GPR56 gene (upper panel) and the encoding receptor protein (lower panel). The GPR56 gene consists of 14 exons, of which the exons 2–14 code for the receptor protein. The figure depicts the full-length GPR56 gene with a length of 2082 base pairs (Intron: line; Exon: solid bar; coding region: blue; non-coding region: red). The corresponding wild-type (WT) protein isoform is composed of 693 amino acids (Signal Peptide: red; PLL domain-β sheet A: yellow; PLL domain-β sheet B: green; GAIN-subdomain A: purple; GAIN-subdomain B: dark green; GPS region and Stachel peptide: pink; TM regions: orange; Intracellular and extracellular loops: cyan) [16,22]. (B) Schematic diagrams depicting the four GPR56 alternatively spliced isoforms, S1–S4. The corresponding protein structures are depicted below the gene structure [16,22,24]. (C) The schematic cartoon of the structural organization of GPR56 receptor protein. ICR: Intracellular Region.