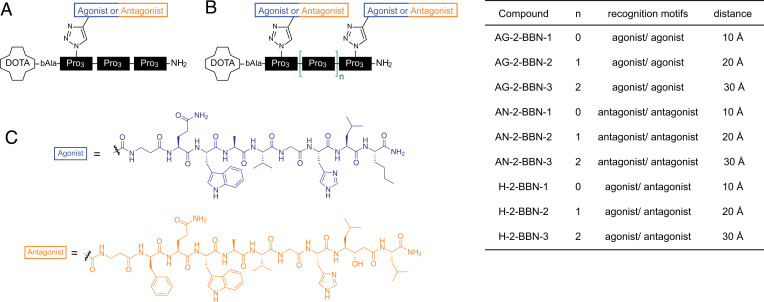
Fig. 1.
Overview of used compounds. (A) AG-1-BBN-1 as an example for a monovalent compound. All monovalent compounds contain three blocks of three prolines. Agonists/antagonists were coupled to block 1, 2, or 3. (B) Bivalent ligands consists of two to four oligoproline blocks. The first ligand is always attached to block 1. The second ligand is linked to block 2, 3, or 4, resulting in bivalent ligands with a distance of 10, 20, and 30 Å between recognition motifs. Nomenclature and distances are given on the right side. (C) Chemical structures of the agonist (AMBA) and the antagonist (RM1).