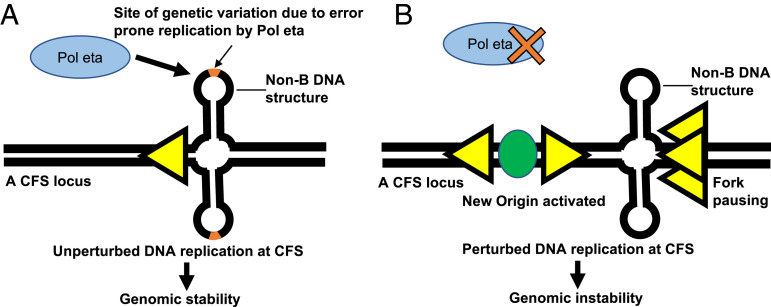
Fig. 6.
Model depicting the role of Pol eta in the replication of CFS. (A) Pol eta facilitates replication of CFS and maintains genomic stability. Pol eta is a translesion Pol that lacks an efficient editing function. Thus, when Pol eta replicates CFS, genetic variation can occur at certain sites, including those containing non-B DNA structures. These sites correspond to the regions of replication-fork pausing in the cells that are deficient for Pol eta (shown in B). (B) Deficiency of Pol eta leads to perturbed DNA replication and genomic instability at CFS. In the absence of Pol eta, replication forks pause (overlapping yellow arrowheads) at certain sites, including those containing non-B DNA structures. This is accompanied by new origin activation (green oval).