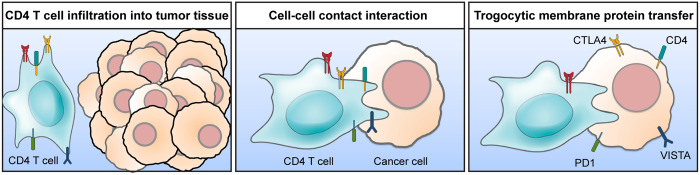
Fig. 6.
Schematic illustration. Hematopoietic cells including CD4 T cells infiltrate into tumor tissues. Tumor-infiltrating hematopoietic cells interact with cancer cells in the tumor microenvironment. During the cell–cell contact interaction, cancer cells acquire membrane proteins from the contacted hematopoietic cells by trogocytosis. Unlike phagocytosis or entosis, which internalize endocytosed materials into the cytosol, trogocytosis maintains cell surface localization of the transferred membrane proteins. Trogocytic transfer of immune modulatory proteins, such as CTLA4, LAG3, PD1, Tim3, VISTA, and CD38, contributes to develop the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment.