Figure 6.
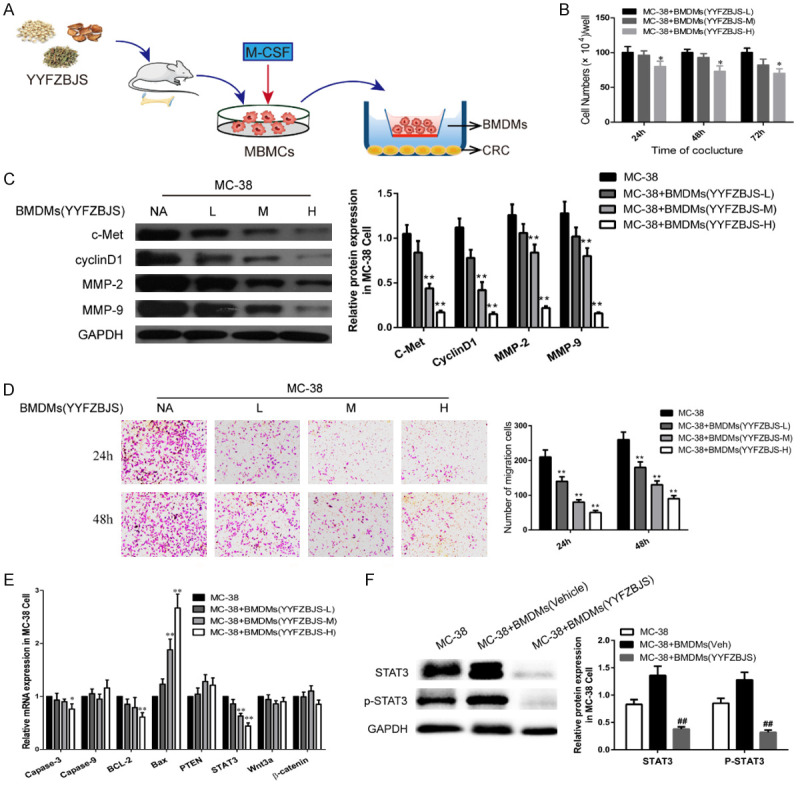
YYFZBJS inhibited tumor cell proliferation through regulating ETBF primed BMDMs in vitro. A. Experimental design indicating bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) were isolated from the bone marrow of C57BL/6J mice treated with or without YYFSBJS at the doses of 3.825 g/kg, 7.65 g/kg and 15.3 g/kg for 2 weeks. The BMDMs were from femurs and tibias of mice and cultured in a special medium (DMEM containing 10% FBS supplemented with 50 μg/ml penicillin/streptomycin and 10 ng/ml recombinant macrophage colony-stimulating factor [M-CSF; Thermo Fisher Scientific]). Then the primed BMDMs (TAM) were collected and were assigned to MC-38 cells in a 10:1 ratio. B. MC-38 cells proliferation was assayed at 24, 48, and 72 h after co-culture with the M2φ. The data are presented as the mean ± SD from at least three experiments. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs. MC-38+BMDMs (YYFZBJS-L). C, F. Western blot and quantitative assay of c-Met, cyclinD1, MMP-2, MMP-9, STAT3 and phosphorylation of STAT3 in MC-38 cells. GAPDH is the loading control. The data are presented as the mean ± SD from at least three independent experiments. **P<0.01 vs. MC-38; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs. MC-38+TAM (Veh). D. Cell invasion assay result using Matrigel-coated Transwell. (left, representative pictures of invasion chambers; right, average counts from five random microscopic fields). Data are presented as mean ± SD of triplicate experiments. **P<0.01 vs. MC-38. E. mRNA expression of genes associated with cell proliferation in MC-38 cells was evaluated using quantitative RT-PCR. The data are presented as the mean ± SD from at least three experiments. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs. MC-38.
