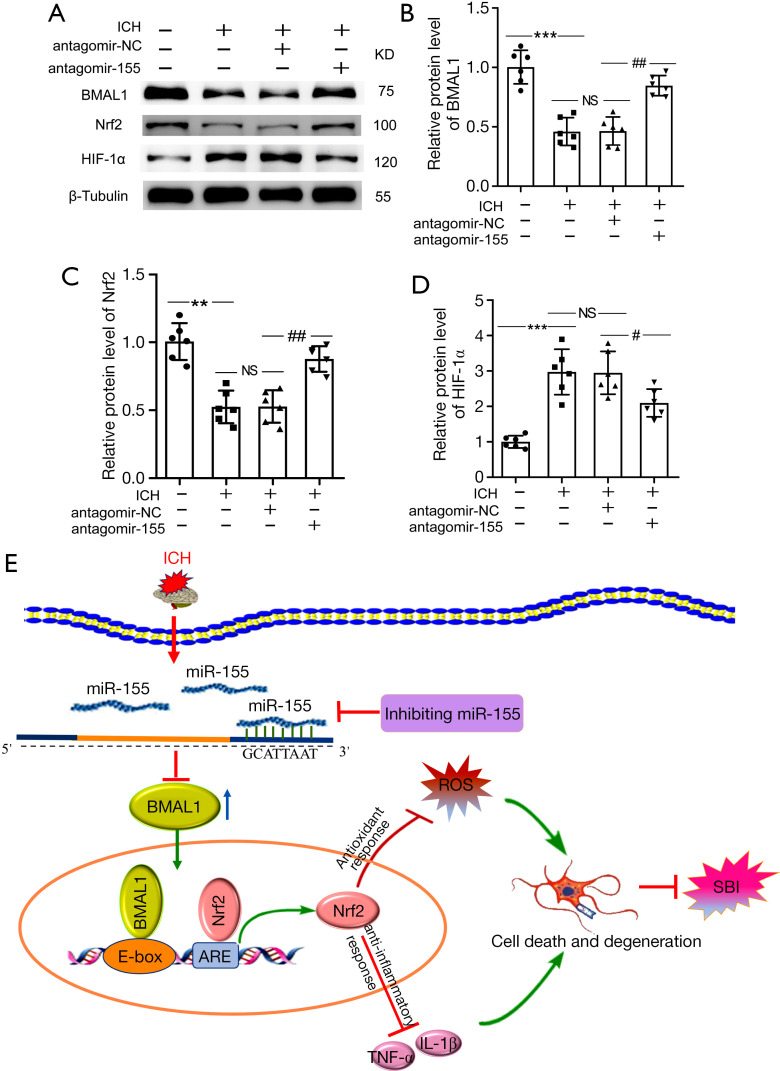
Figure 7.
Effects of increased BMAL1 on the Nrf2 signaling pathway after ICH. (A) Western blot analysis of the relative levels of the BMAL1, Nrf2 and HIF-1α proteins in the sham, ICH, ICH + antagomir-NC and ICH + antagomir-155 groups at 24 h after ICH; (B) Western blot analysis of the relative levels of the BMAL1 protein in the groups listed above; (C) Western blot analysis of the relative levels of the Nrf2 protein in the groups listed above; (D) Western blot analysis of the relative levels of the HIF-1α protein in the groups listed above; (E) Schematic representation of the role and related mechanism of BMAL1 in SBI after ICH. The BMAL1 protein level decreased in the brain tissue of rats after ICH. After antagomir-155 treatment, the BMAL1 protein was upregulated, and then the Nrf2 signaling pathway was activated to attenuate SBI induced by ICH, including oxidative stress, inflammation, and neuronal death. All data are presented as the mean ± SEM. ***P<0.001 vs. Sham group; **P<0.01 vs. Sham group; ##P<0.01 vs. ICH + antagomir-NC group; #P<0.05 vs. ICH + antagomir-NC group; NS, no significant difference vs. ICH group; n=6. ICH, intracerebral hemorrhage; NC, negative control; SEM, standard error of mean.