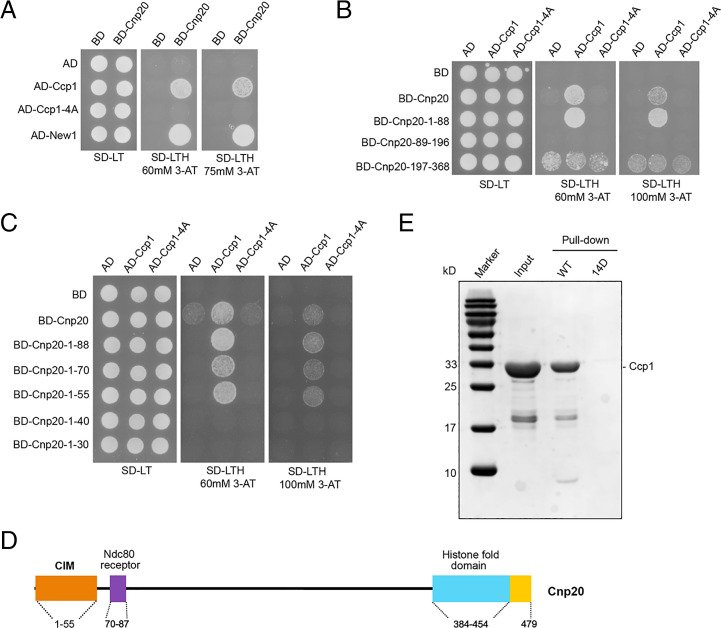
Fig. 3.
The N terminus of CENP-T contains a conserved CIM. (A) Yeast two-hybrid (Y2H) analysis confirmed the interaction between Ccp1 and CENP-TCnp20 and also showed that the interaction is lost in the dimeric mutant of ccp1-4A. S. cerevisiae strains carrying the indicated plasmid combinations were spotted onto synthetic defined (SD) minimal medium plates lacking either Leu and Trp (SD −LT) or Leu, Trp, and His (SD −LTH) supplemented with either 60 mM 3-amino-1,2,4-triazole (3-AT) or 75 mM 3-AT, and grew at 30 °C. AD, activation domain; BD, binding domain. (B) Y2H assays indicated that Ccp1 associates with the first 88 amino acids at the CENP-TCnp20. (C) The first 55 amino acids of CENP-TCnp20 were identified by Y2H as a minimum Ccp1-interacting motif. (D) A schematic diagram of the domain structure of CENP-TCnp20. Orange, the CIM domain; cyan, histone fold domain; purple, Ndc80 receptor motif. (E) In vitro pull-down assay demonstrates that the first 55 amino acids of CENP-TCnp20 interact with Ccp1, but the interaction of the phosphomimetic 14D mutant of the region (14D) with Ccp1 is disrupted. Wild-type and phosphomimetic 14D mutant peptides derived from Cnp201-55, and purified full-length Ccp1 were used.