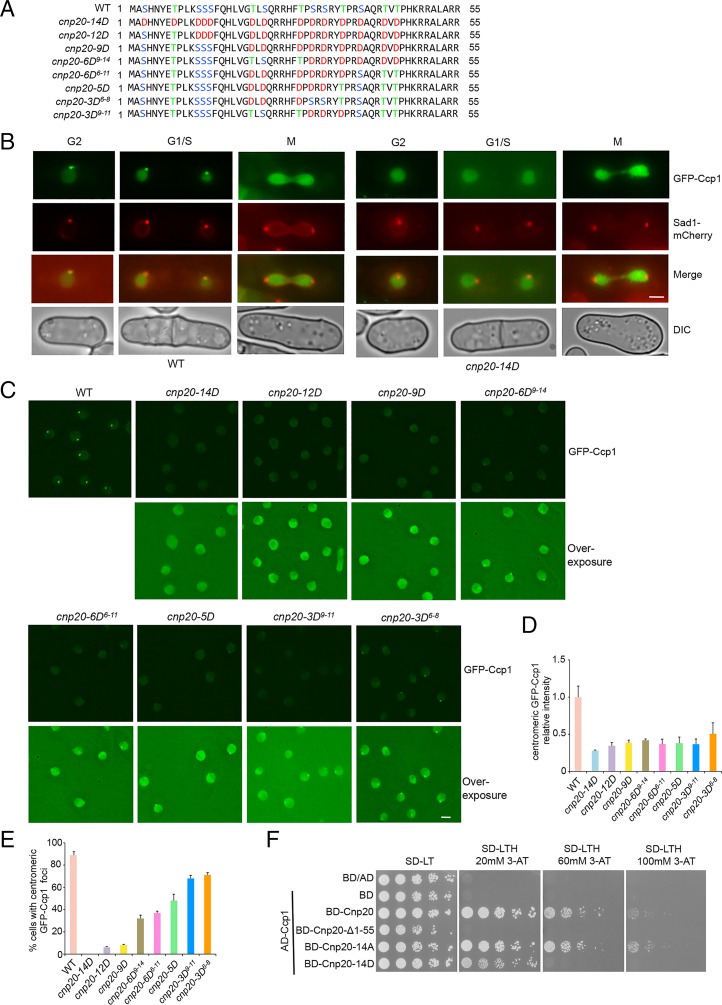
Fig. 5.
The association of Ccp1 with centromeres is abolished in the cnp20-14D mutant. (A) Schematic representation of the wild-type CIM domain and its phosphomimetic mutants. (B) Ccp1 dissociates from centromeres through all stages of the cell cycle in the cnp20-14D mutant. Sad1-mCherry was used as an SPB marker. (C) The distribution pattern of GFP-Ccp1 in indicated phosphomimetic mutants. Wild-type cells carrying GFP-Ccp1 were used as a control. (D) Quantification of relative fluorescence intensity of centromeric GFP-Ccp1 in the indicated cells. At least 40 cells were scored in one single experiment. Error bars represent mean and SD. (E) Quantification of the percentage of cells showing centromeric localization of GFP-Ccp1 in the indicated cells. Experiments were performed in triplicate. At least 40 cells were scored in one single experiment. Error bars represent mean and SD. (F) The Y2H analysis indicated that the interaction of Ccp1 with phosphomimetic Cnp20-14D mutant was weakened. (Scale bars, 2 μm.)