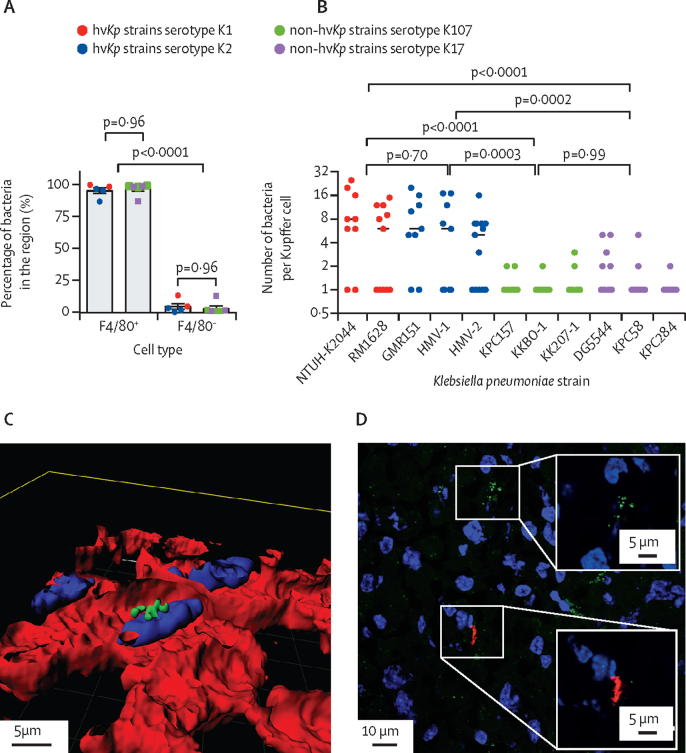
Figure 1.
Tissue tropism and intracellular localisation of Klebsiella pneumoniae in mouse livers 6 h after intravenous infection
(A) Quantitative distribution of K pneumoniae in F4/80+ and F4/80− cells in the mouse liver. Data are representative of two entire tissue sections of approximately 2 × 2 cm per mouse. (B) Size of bacterial clusters associated with Kupffer cells at 6 h after infection. 30 random fields of view were analysed with a 60 × magnification with the Olympus confocal microscope. Circles represent individual bacterial clusters. (C) 3D reconstruction using Imaris 3D V9.4 of a K1 foci of infection Z-stack acquired on the confocal microscope showing the top of the cell layer, and a single cut into the cell. DAPI stain indicated in blue, F4/80 in red, and K1 ST23 in green. (D) K1 and K2 co-infected tissue section stained with purified IgG raised against K1 (green) capsule, or K2 (red) indicating two monochrome bacterial foci. A higher magnification of each monochrome focus is shown in insets. Lower magnification co-localisation images for all serotypes, in addition to confocal Z-stacks are shown in the appendix (pp 7–8). DAPI=4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole. hvKp=hypervirulent K pneumoniae.