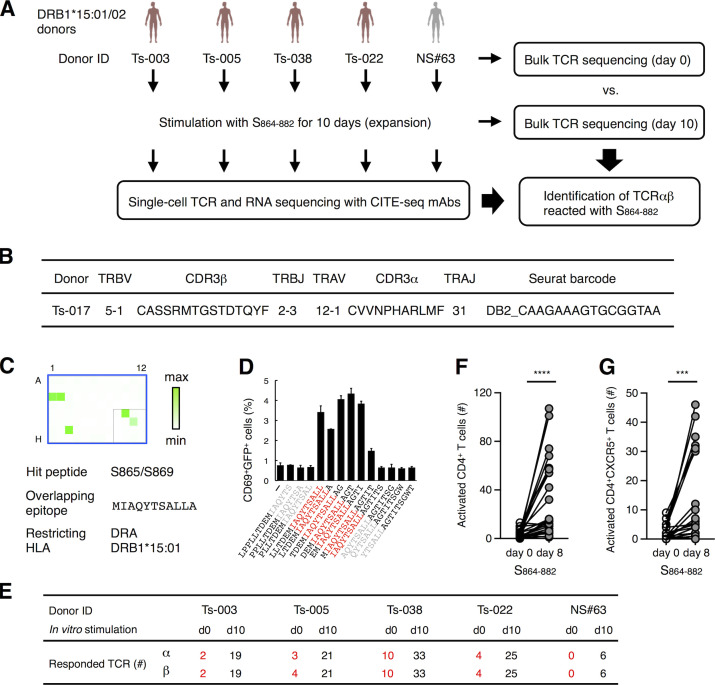
Figure 6.
Characterization of S864–882-reactive T cells. (A) Workflow of the analysis for the S864–882-induced T cell expansion. PBMCs from convalescent COVID-19 patients (red) and healthy (gray) donors possessing DRB1*15:01 or *15:02 were analyzed by bulk TCR-seq or stimulated with 1 μg/ml S864–882 peptide for 10 d before CD4+ T cells were sorted and analyzed by single-cell TCR- and RNA-seq as well as bulk TCR-seq. (B) V and J usages and CDR3 sequences of the newly identified clonotype that recognizes S870–878 epitope. (C) Reporter cells expressing TCRαβ in B were stimulated with pooled peptide matrix described in Fig. S3 A in the presence of DRA-DRB1*15:01–expressing APCs. Wells containing S865 or S869 (C1, C2, and G3), S pool #2 (E10), and S864–882 (F11) were positive. (D) 1 μg/ml of serial overlapped 15-mer peptides covering the S861–887 region were tested for reactivity to the clonotype in B to determine the minimum epitope (shown in red). Data are shown as mean ± SD of triplicates. (E) Numbers of TCRα and β of expanded clonotypes (proportion >0.1% in single-cell TCR-seq) detected in bulk TCR-seq described in Table S4 are shown. (F and G) 105 of PBMCs from healthy donors were left unstimulated (day 0) or stimulated with S864–882 for 8 d (day 8). Numbers of CD4+CD69+CD137+ T cells (F) and CD4+CD69+CD137+CXCR5+ Tfh cells (G) are shown. Data are representative of two independent experiments (C and D). ***, P < 0.005; ****, P < 0.001. ID, identifier.