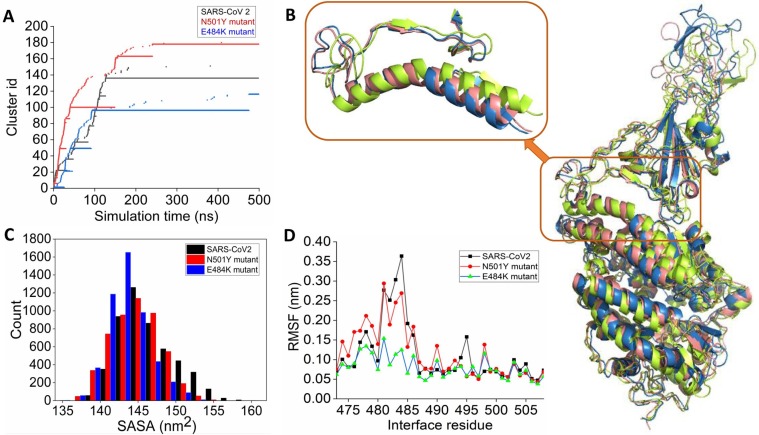
Fig. 2.
(A) Time-evolution of conformational clusters evident from the RMSD based clustering of simulation trajectory of wild-type (black), N501Y (red), and E484K (blue) RBD complexed with ACE2. (B) The alignment of the average complex structure from the most populated clusters for the three systems is shown. Wild-type, N501Y, and E484K RBD complexed with ACE2 are colored as deep salmon, greenish-yellow, and blue, respectively. (C) Distribution of the solvent-accessible surface area (SASA) of wild-type and mutant RBDs obtained from the simulations of three RBD-ACE2 complexes. (D) Root mean square fluctuations (RMSF) of the receptor binding motif obtained from the simulations of RBD-ACE2 complexes. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)