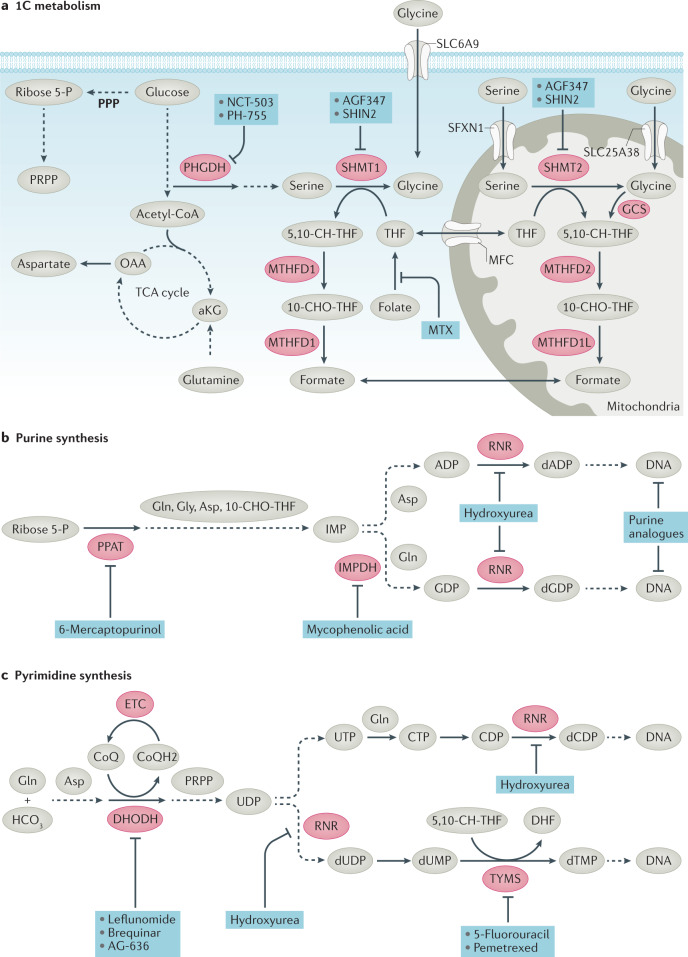
Fig. 5. Inhibitors of nucleotide synthesis.
a | One-carbon (1C) metabolism. Nucleotide synthesis uses ribose 5-P produced by the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) and aspartate produced from oxaloacetate, as well as glycine and tetrahydrofolate methyl donors — methylene-THF (5,10-CH-THF) and formyl-THF (10-CHO-THF) — arising from 1C metabolism linked to the conversion of serine to glycine. 1C metabolism occurs in both the cytoplasm and mitochondria. b | Purine synthesis is a multistep, multienzyme pathway that uses ribose 5-P, glutamine (Gln), glycine (Gly), aspartate (Asp) and 10-CHO-THF to make inosine monophosphate (IMP). IMP is converted to ADP and GDP, which can then be converted to dADP and dGDP. c | Pyrimidine synthesis is a multistep process that uses phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate (PRPP) as a scaffold to produce UDP from glutamine, carbonate and aspartate. Ribonucleotide reductase (RNR) converts UDP to dUDP and CDP to dCDP. Thymidylate synthase (TYMS), which can be inhibited by the clinical agents pemetrexed or 5-fluorouracil (5-FU), converts dUMP to dTMP. CoQH2, reduced Coenzyme Q; DHF, dihydrofolate; DHODH, dihydroorotate dehydrogenase; ETC, electron transport chain; GCS, glycine cleavage system; HCO3, bicarbonate; IMPDH, inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase; MTHFD1, methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase 1; MTHFD1L, methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase 1-like; MTHFD2, methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase 2; MTX, methotrexate; PHGDH, phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase; PPAT, phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate amidotransferase; RNR, ribonucleotide reductase; SHMT1, serine hydroxymethyl transferase 1.